What types of indicators are there?
Here are the absolute migration rates:
- number of people who came to the region (urban region) – P;
- number of departed persons – B;
- migration net or balance - MS;
- migration turnover (gross or volume) – MO.
There are several indicators that characterize demographic processes, in particular the general migration increase. To analyze statistical data, the concept of “migration balance” is often used. This is an absolute value. It is influenced by the population size in a certain area.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=
For calculations you will need several coefficients. These include:
- P – number of arrivals to the region.
- B – number of people leaving the region.
- MS – migration net or balance.
The amount of population growth due to migration is calculated very simply. It is equal to the difference between those who arrived and those who left a given territory. That is, in the form of a formula, this can be represented as MS = P-V. This indicator can be both positive and negative. If the number is less than zero, then we are talking about the concept of “migration loss”. For the opposite result, a positive value is required.
The second method is also possible. If the total and natural increase is known, then by subtracting the second from the first, the required value can be obtained. This will be mechanical population growth.
Relative values for specific population groups are also calculated. For example, this is the number of visitors per a certain number of local residents (most often per thousand). In the form of a formula, it looks like Kpr=(P/N)*1000. Kpr is the arrival rate.
To increase accuracy in statistics, it is better to calculate average values over several years. This data is necessary to analyze the current situation, determine immigration policy and manage labor resources.
Relative values for specific population groups are also calculated. For example, this is the number of visitors per a certain number of local residents (most often per thousand). In the form of a formula, it looks like Kpr=(P/N)*1000. Kpr is the arrival rate.
Mortality is a demographic process that includes the totality of deaths in a population over a certain period of time (usually a year). The mortality rate is influenced by many factors, which are divided into four important groups: 1. natural biological factors - heredity, environmental conditions, etc.; 2.
socio-economic factors - lifestyle, standard of living, nature and working conditions, development of the healthcare system, war, etc.; 3. demographic (structural) factors - gender, age, marriage, territorial, etc. population composition; 4. factors that contribute to mortality: smoking, alcohol, drugs, etc.
M - Total number of deaths (Characterizes the absolute scale of the mortality process) Mi - Partial number of deaths (Characterizes the composition of the dead by gender, age, territory, months of the year, etc.) General mortality rate (Characterizes the number of deaths per 1000 population)
(Characterizes the number of deaths per 1000 people of a particular population group, for example, men or women) (Characterizes the number of deaths per 1000 people of the same age) - average annual population; — average annual number of men (women); Mx is the number of deaths at a certain age; - average annual population at a certain age. The total and private numbers of deaths reflect the absolute scale of mortality, but say nothing about its intensity. The overall mortality rate, despite its simplicity of calculation and clarity, should be recognized as a rough estimate due to its serious dependence on the structure of the population (primarily, age and gender). The partial mortality rate repeats all the advantages and disadvantages of the general rate. The age-specific mortality rate serves as the most accurate indicator of mortality intensity. If it is calculated differentiated by gender, it eliminates the influence of the gender and age structures of the population.
Let's look at what the absolute indicators of population migration are:
- number of arrivals (to region, locality, region) (P);
- number of departed (B);
- migration balance (or net) (MS);
- migration volume, or gross, or turnover (MO).
MS = P-V
This value can be positive, negative or zero. In the first case they talk about population growth, in the second – about its decline.
If it is known what the total population growth and its natural increase (due to births and deaths) are, the mechanical increase can be calculated as the difference between the first and the second.
Volume of migration
MO = P V.
All these indicators are specific numbers that depend on the population of the area, and therefore cannot give a complete picture of what is happening, that is, an idea of the intensity of the processes. Therefore, relative characteristics, such as the migration rate, are also needed.
There are general and specific coefficients, as well as indices of the relative intensity of movements for individual groups:
- The arrival rate shows the number of arrivals for every thousand people living in a region in one year:
Kpr = (P/N)x1000
where N is the average annual number of people living in a given territory;
- The departure rate shows how many people have left for every thousand residents in a year:
Cube = (W/N)x1000;
- migration turnover coefficient:
Kmo = ((P V)/N)x1000;
- migration balance coefficient:
Kms = ((P – V)/N)x1000;
- migration efficiency coefficient – ratio of balance to turnover as a percentage:
Cam = ((P -V)/(P V))x100;
- relative migration balance - the ratio of the number of arrivals to the number of departures as a percentage:
MCo = (P/V)x100.
Having made calculations for various groups of residents (age, gender, nationality), we obtain specific characteristics.
You can also calculate averages over several years: this is done in order to avoid random deviations in values. To calculate in this case, average absolute indicators and data on the number of residents for the required period are taken.
To have an idea of what share individual groups occupy in the total number of arrivals or departures, relative intensity indices are calculated for them.
When talking about indicators of statistics on external migration of the population, they use the words “emigration”, “immigration”, and also make calculations for a separate group - labor migrants.
3. Migration growth rate, according to the formula
= (P-W/S) *1000 (1.11)
(2006) = ( (13600_15100) /1164000) *1000 = — 1,3
It can be seen that the number of people leaving the region exceeds the number of people arriving in it.
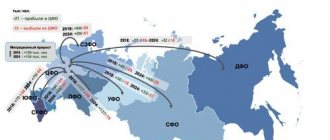
Let us present another diagram in order to visually compare the number of those who entered the region and the number of those who left it.
Figure 2.20 - Number of arriving and departing migrants in 2005 - 2007
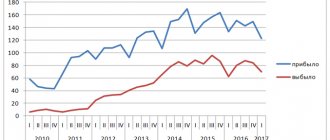
4. Migration intensity coefficient - the total number of arrivals and departures per 1000 people of the average annual population is calculated as
Com = (Ohm/S) * 1000 (1.12)
Com (2007) = (28700/11 64000) * 1000 24.6
Thus, approximately 24.6 people per thousand of the average annual population entered and left the region.
And in previous years, the intensity coefficient has been growing, mainly due to the excess of the number of departing migrants over the number of arrivals.
3. Factor analysis and statistical forecasting of population statistics indicators 3.1 Factor analysis of population movement indicators
Before conducting a factor analysis of population movement indicators, it is necessary to determine what still relates to these indicators. First of all, these are indicators of fertility, mortality, and migration.
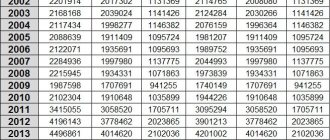
Table 3.21 - Number of births and deaths in the Kursk region for the period 2005 - 2007
| The name of indicators | 2005 year | 2006 | 2007 |
| 1. Average annual population, people. | 1191500 | 1177300 | 1164000 |
| 3. Number of deaths, people. | 10247 | 10596 | 10626 |
| 23473 | 22487 | 22650 |
You can use the method of chain substitutions to characterize the influence on natural growth of two indicators: the number of births and the number of deaths.
=NM (1/4)
Where N is the number of births,
M is the number of deaths.
= — (3.13)
, — those born and died in the base year.
conv = — (3.14)
natural increase due to the number of births in the reporting year and
number of deaths in the base.
= — (3.15)
natural increase due to the number of births and deaths in the reporting year.
, — those born and died in the reporting year.
Now let’s look at the influence of factors on natural growth; we’ll take 2006 as a base and 2007 as the reporting period.
= 10596-22487 = - 11891 people.
That is, the number of deaths in 2006 exceeds the number of births in the same year by 11,891 people.
conv = 10626-22487= - 11861 people.
The number of deaths in 2006 again exceeded the number of births in 2007 by 11,861 people.
Let's see how the number of births affects natural growth: eats = conditional -
eats = - 11861 11891 =30, = 10626-22650 = - 12024
eats = -conv
eats = -12024 11861 = - 163
That is, if we consider the influence of two factors, the number of births and the number of deaths, then in this case the second factor has a greater influence, because the number of births changes, or rather increases the population by 30 people, and the number of deaths reduces it by 163 people.
Types of values
Absolute migration indicators include the following values:
- the number of citizens arriving in the territory (region, locality). Designated as "P";
- the number of people who left the point - “B”;
- balance or net “MS” or “N”;
- volume (gross or turnover) - “MO”.
Read also: How to get a child’s passport
The volume indicator is not a type of migration, like the balance. This indicator is calculated based on the sum of the number of arrivals and departures in a certain region over a period of time.
The migration balance itself is usually divided into:
- external - displaying the difference between those who arrived and left a specific region;
- internal - shows movement throughout the country;
- different population groups - depending on nationality.
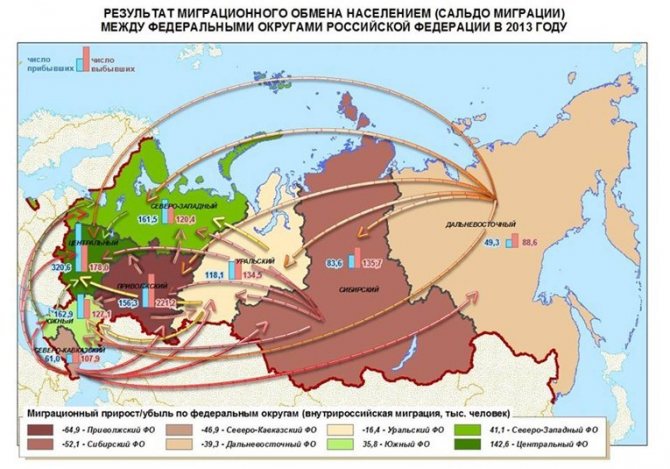
Balance of migration in 2013
What is mechanical gain and how is it calculated
As already mentioned, the migration balance is an indicator of the difference between citizens who arrived and left the country. A simple formula is used for the calculation - “MS” equals “P” minus “B”.
The value can be positive, negative or zero. If there is information about general population growth and natural growth (fertility minus mortality), then mechanical values can be calculated using the specified data.
Volume of migration
To calculate the volume, you will need to use data on citizens who arrived and left a certain territory during a specified period of time. The calculation is as follows: “MO” is equal to “P” plus “B”.
The indicated indicators are specific numbers that are influenced by the indicators of a certain territory. As a rule, the meanings themselves cannot describe the entire situation as a whole. It is for this reason that an additional indicator such as the migration rate is used.
General definition of migration
The very concept of “migration” can be deciphered as a change of place of residence or relocation. This definition is one of the key ones in demographic processes, because the life of the state directly depends on this action. It affects the population of the country and, accordingly, the economic situation.
What is migration growth? The concept is defined in demography as the difference between those who arrived in a territory for permanent residence and those who left it irrevocably.
Migration processes are divided according to several classification criteria:
- to size;
- according to form;
- because of;
- the nature;
- by time;
- by legal status.
The very concept of “migration” can be deciphered as a change of place of residence or relocation. This definition is one of the key ones in demographic processes, because the life of the state directly depends on this action. It affects the population of the country and, accordingly, the economic situation.
Mechanical population growth
MS=P-V
This indicator can be negative (population decline), positive (increase) or equal to 0.
If there is data on the general and natural population growth, you can calculate the mechanical growth as the difference between the 1st and 2nd.
There is a second way to calculate migration growth in the case when the total and natural increase is known. Mechanical growth is obtained by subtracting natural growth from total growth.
KP=(P/N)*1000.
KP – arrival coefficient,
P number of visitors,
N – number of local residents.
To obtain more accurate statistical indicators, average values are calculated over several years, which makes it possible to analyze the current situation, determine immigration policy and manage labor resources.
KP=(P/N)*1000.
MS=P-V
KP=(P/N)*1000.
MS=P-V
MS=P-V
KP=(P/N)*1000.
MS=P-V
There is a second way to calculate migration growth in the case when the total and natural increase is known. Mechanical growth is obtained by subtracting natural growth from total growth.
KP=(P/N)*1000.
MS=P-V
KP=(P/N)*1000.
What classifications exist
The migration balance allows you to determine the rate of mechanical growth.
However, when making calculations, additional nuances should be taken into account. The classification indicator is of great importance. Important! Only current data is used in the calculation and it must be completely reliable.
However, even in this case it is impossible to avoid certain errors. It is for this reason that the classification of indicators is usually divided into absolute and relative.
These values help make more accurate calculations. However, even these should be treated with a small amount of skepticism, with the addition and subtraction of a certain proportion of the number.
Absolute
The absolute category of classification usually includes:
- the total number of persons arriving in the country. The meaning is used both in relation to the entire state and in specific areas and settlements;
- the total number of citizens who left the specified territory for another state for permanent residence or work;
- migration balance - the difference between arrivals and departures;
- volume of migration.
When calculating, internal and external values are used, as well as reference to a specific indicator, such as nationality.
Relative
The following values are usually included in this group:
- arrival rate - a formula is calculated to determine the number of immigrants per population of a thousand people. Formula: “P” is divided by “N” and multiplied by 1000;
- departure rate - denotes the total number of emigrants per 1000 population. It is calculated by the formula: “B” is divided by “H” and multiplied by 1000;
- migration turnover - calculated by adding the number of citizens arriving and leaving the country by a certain number of population. Formula: “P” is added to “B”, the result is divided by “N” and multiplied by 1000;
- balance - a number value for a certain amount of population living in the territory of the state. Calculation: “P” minus “B”, the result is divided by “N” and multiplied by 1000;
- migration efficiency - the indicator is calculated using the values of balance and migration turnover. Expressed as a percentage. Formula: “P” minus “B”, the result is divided by the sum of “P” and “B” and multiplied by 1000;
- relative - the ratio between the number of people arriving and leaving the country, expressed as a percentage. Formula: “P” is divided by “B” and multiplied by 100.
Read also: Illegal migration
Episodic migrations
There are four main types of spatial population movement that determine migration growth.
Episodic migrations periodically affect the number of inhabitants. Thanks to them, at one moment the number of residents in a locality can become many times greater. These are, as a rule, trips related to recreation and tourism, business and others. They have no time frame or set direction. The individuals involved in this type of spatial movement can be quite different. If these are business trips, then, of course, able-bodied citizens travel. But when it comes to recreation, the contingent becomes wider.
Since episodic migration growth is difficult to explain and is only temporary, it is practically not studied. Although this is despite the fact that this type of spatial movement is the most large-scale, especially in the field of tourism.
Episodic migrations periodically affect the number of inhabitants. Thanks to them, at one moment the number of residents in a locality can become many times greater. These are, as a rule, trips related to recreation and tourism, business and others. They have no time frame or set direction. The individuals involved in this type of spatial movement can be quite different. If these are business trips, then, of course, able-bodied citizens travel. But when it comes to recreation, the contingent becomes wider.
Pendulum migrations
This type of movement is determined by the need of the population for constant travel. Participants in pendulum migration are residents of both urban and rural areas. Most often, this type of migration refers to daily trips to work or study. It is most clearly expressed where there is any possessive center.
Commuting migrations contribute to changes in the structure of labor resources. Thanks to this, vacancies are filled by people living in settlements where there are no job opportunities.
This type of population movement has virtually no effect on migration growth, unless in the process a person decides to change his place of residence.
Problem solving
Let's try to solve 2 types of problems.
- How to find the migration increase from the table?
| Types of migration | Number of arrivals, people | Number of people leaving, people |
| Migration within the country | 1 940 000 | 1 940 000 |
| Within regions | 1 750 000 | 1 750 000 |
| Between regions | 190 000 | 190 000 |
| International (for permanent residence) | 26 000 | 15 000 |
To determine migration growth, only international migration needs to be counted. We use the formula: MP = P – B = 26,000 – 15,000 = 11,000 people.
- How to determine population growth in a region for a particular year?
Data: number of arrivals for permanent residence = 40,000 people; number of people leaving for permanent residence = 10,000 people; natural increase (NU) people/year = 3500 people.
We act in 2 stages:
MP = P – V = 40,000 – 10,000 = 30,000 (persons)
Total increase = MP + EP = 30,000 + 3500 = 33,500 (persons)
When receiving negative values, the sign must be taken into account when calculating, as in a regular mathematical operation.
Seasonal migrations
This category includes people who, for some reason, were forced to leave their permanent place of residence for an indefinite period.
Thanks to this type of movement, the labor shortage is filled and production needs are satisfied. The reason for this process is the uneven distribution of economic levels in the regions. The latter is due to the fact that certain industries generate more income. That is, in such places there is always a need for workers. If local resources cannot replenish it, then additional ones are attracted from other regions.
Most often, this movement is caused by seasonal industries. This is agriculture (mainly sowing and harvesting), logging and coastal fishing.
This category includes people who, for some reason, were forced to leave their permanent place of residence for an indefinite period. Thanks to this type of movement, the labor shortage is filled and production needs are satisfied. The reason for this process is the uneven distribution of economic levels in the regions.
This category includes people who, for some reason, were forced to leave their permanent place of residence for an indefinite period. Thanks to this type of movement, the labor shortage is filled and production needs are satisfied. The reason for this process is the uneven distribution of economic levels in the regions.