Salary per month by profession in 2021
The highest average wages were recorded among officials, as well as in the field of information technology and the financial sector. The smallest are in trade and services.
Living wage
The Estonian government has set a poverty line of 150 euros. This is the amount that a low-income person should have left after paying for housing. In this case, certain benefits are provided. In 2021, certain social security amendments were passed. Thanks to this, the subsistence allowance calculation system has become more flexible.
The subsistence allowance is government assistance to people in need. These payments come from local government. When determining this amount, the minimum expenses for shoes, clothing and food are taken into account. In addition, the size of the living area is calculated, as well as the number of rooms and residents.
Minimum
From January 1, 2021, the minimum monthly wage increased from 470 to 500 euros. The minimum hourly wage is 2.97 €.
Average
Monthly earnings vary depending on the profession. So, in the first quarter of 2021 it was before taxes:
| Profession | Payment, €/month |
| Doctor | 1664 |
| Nanny | 470 (minimum payment) |
| Guide | 636 |
| Housemaid | 512 |
| Teacher | 971 |
| High school teacher | 1026 |
| Taxi driver | 954 |
| Dentist | 1692 |
| Loader | 870 |
| Engineer | 1300 |
| Nurse | 922 |
| Welder | 1121 |
| Programmer | 2000 |
| Electrician | 993 |
| Police officer | 1003 |
| Worker | 778 |
| Salesman | 700 |
| Firefighter | 788 |
| Driver | 945 |
| Lawyer (advocate) | 1443 |
| Driver | 1235 |
| Accountant | 993 |
| Builder | 992 |
For seasonal workers, hourly wages ranged from 2.97 to 18 €.
There is a significant gap in wages between men and women, reaching 25%.
Average starting
The starting salary level depends on the qualifications required to perform it. The more complex the professional duties and the more time it takes to master them, the greater the gap between the average and starting salary level. It can reach 20% for the duration of the internship. Most often, graduates of educational institutions and visitors who do not yet have work experience face problems associated with low starting pay.
Maximum
There are no officially approved salary limits. Monthly earnings of over 2,250 euros in the capital, and over 1,600-1,800 for Tartu and other cities in the country are considered high.
Wages in different counties
Almost a third of Estonia's population is concentrated in Tallinn; government bodies and offices of leading commercial enterprises are located here. This led to a significant gap between the average salary in the capital and its district from the rest of the country. So, in 2021 it amounted to 1353 euros.
The next highest salary city is Tartu, where on average residents earn 1,215 euros.
Residents of Saremaa, Jõgevamaa and Põlvamaa counties had the most modest earnings, amounting to 880–900 euros.
Average salary in Tallinn
Every year many young professionals from other cities, some even from Russia, come to Tallinn. It attracts foreigners due to its standard of living, European infrastructure and close distance. New positions in IT technologies are constantly being created here, and this is very attractive for programmers from Russia and Ukraine. The average salary in Tallinn is the highest, from €1000-2000.
Labor market in Estonia
Unemployment in Estonia does not exceed 4%. In some sectors of the Estonian economy there is even a certain shortage of workers, both highly qualified and unqualified. For official employment in Estonia, you must find a vacancy in advance, sign an employment contract, obtain a work permit, open a visa and obtain a residence permit.
In rare cases, for example, for university teachers, athletes, seasonal workers in agriculture and some other professions, a simplified procedure for labor migration to Estonia is provided. But usually EU citizens and Estonians should not apply for a job. It is best to look for work in Tallinn, where over 60% of open jobs in the country are concentrated.
According to official data from the Estonian Statistical Office, the minimum wage in Estonia in 2021 is 584 euros per month. The average salary is 1,396 euros per month, and after taxes 1,155 euros. Depending on the region, salaries in Estonia range from 950 to 1,470 euros per month. The highest salaries were recorded in the field of financial and insurance activities, about 2,400 euros.
The most in-demand professions in Estonia
When looking for a job in Estonia, foreigners should pay attention to the areas of information technology, construction, agriculture and road transport. Most often, truck drivers, IT specialists, medical personnel and technical professionals are required. In recent years, Estonia has experienced a surplus of trade workers and some blue-collar workers.
Important . According to a study on labor force needs conducted by the Estonian Unemployment Insurance Fund (EUIF), programmers, cooks and truck drivers will be most in demand on the Estonian labor market in the coming years.
Revenue by industry
The Estonian Statistics Authority provides the following data on income in different industries:
| Industry | Average monthly income, euro | Average monthly income, rub. |
| Insurance, finance and banking | 2 411 | 171 600 |
| Supply of gas, electricity, air conditioning | 2 264 | 161 137 |
| Communications, information and communication | 2 195 | 156 226 |
| Mining industry | 1 667 | 118 601 |
| Public administration | 1 658 | 117 960 |
| Scientific, technical and professional activities (specialists with higher education who belong to other industries) | 1 458 | 103 731 |
| Social work and health | 1 361 | 96 830 |
| Transport, warehousing, logistics | 1 309 | 93 130 |
| Waste management, water supply, housing and communal services | 1 304 | 92 775 |
| Manufacturing sector | 1 277 | 90 854 |
| Construction and maintenance of buildings and structures | 1 270 | 90 379 |
| Trade (wholesale and retail) | 1 266 | 90 093 |
| Education | 1 246 | 88 670 |
| Administrative and other services | 1 138 | 80 984 |
| Agriculture, forestry, fishing | 1 121 | 79 775 |
| Entertainment, art | 1 102 | 78 422 |
| Real estate transactions | 1 012 | 72 018 |
| Catering, hotel business | 858 | 61 058 |
Each industry employs a large number of specialists with different experience and qualifications, in different positions, so average salaries do not fully reflect the real picture. Here is how much representatives of specific professions receive:
| Profession | Average salary, euro | Average salary, rub. |
| Programmer | 2 000 | 142 328 |
| Dentist | 1 692 | 120 395 |
| Specialist doctor | 1 664 | 118 402 |
| Lawyer, advocate (except private practice) | 1 443 | 102 677 |
| Engineer | 1 300 | 92 502 |
| Driver | 1 235 | 87 877 |
| Welder | 1 121 | 79 765 |
| High school teacher | 1 026 | 73 006 |
| Police officer | 1 003 | 71 369 |
| Electrician | 993 | 70 657 |
| Accountant | 993 | 70 657 |
| Builder | 992 | 70 588 |
| Taxi driver | 954 | 67 884 |
| City transport driver | 945 | 67 244 |
| Nurse | 922 | 65 607 |
| Loader | 870 | 61 907 |
| Firefighter | 788 | 56 072 |
| Shop assistant | 700 | 49 810 |
| Guide | 636 | 45 279 |
| Housemaid | 512 | 36 451 |
| Nanny | from 470 | from 33 560 |
In Estonia, the salary of people with higher education is 20% higher than the national average. At the same time, teachers' salaries are 10% lower than the average earnings of Estonians.
Salaries by profession
The choice of specialty significantly affects wages. The highest paying positions are found in growing industries. Let's look at salary levels depending on the position:
| Profession | Average salary, euro | Average salary, rubles |
| Government officials | 3000 | 218900 |
| Programmers | 2000 | 145900 |
| Dentists | 1690 | 123300 |
| Doctors | 1660 | 121170 |
| Lawyers | 1440 | 105100 |
| Engineers | 1300 | 94800 |
| Machinists | 1230 | 89780 |
| Teachers | 1020 | 74400 |
| Policemen | 1000 | 73000 |
| Electricians | 990 | 72200 |
| Accountant | 990 | 72200 |
| Builders | 990 | 72200 |
| Drivers | 945 | 68980 |
| Loader | 870 | 63500 |
| Firefighters | 780 | 56930 |
| Workers | 770 | 56200 |
| Sellers | 700 | 51000 |
| Guides | 630 | 45980 |
| Maids | 510 | 37200 |
| Nannies | From 470 | From 34300 |
As can be seen from the overview table, simple blue-collar jobs are paid no less worthy than managerial positions. Of course, the difference is noticeable, but with the income level of a simple loader you can live very well in the country.
Salary taxes
In Estonia, several types of tax payments are withheld from wages:
- Income tax.
- Unemployment insurance.
- Pension contributions.
Only income tax in the amount of 21% is deducted from the wages of non-resident employees. If such an employee works under a contract outside Estonia, this deduction is not made.
Income tax
The income tax rate for individuals is 20%. But from January 1, 2021, a tax-free amount has been established, which is up to 500 euros for those whose wages do not exceed 1,200 euros. If the gross salary (before taxes) is more than 1200 euros, but does not reach 2100, the non-taxable minimum is reduced by a coefficient of up to 14%.
To calculate the amount of the non-taxable minimum, you can use the formula 500–500/900*(X – 1200), where X is the amount of the monthly salary.
If the monthly salary is above 2100 euros, tax is paid on the entire amount. Since annual income is taken into account, it includes all bonuses, vacation pay, and disability payments.
Value added tax
The rules for accounting and payment of value added tax are set out in (Käibemaksuseadus). Most transactions are subject to a basic rate of 20%.
The reduced tariff of 9% applies only to sales:
- books and teaching aids;
- medicines and sanitary products for the disabled;
- periodicals, unless they contain advertising or entertainment content for adults;
- services for temporary accommodation of persons.
The zero rate applies to goods exported outside the customs territory of Estonia, transit operations, sales of goods and services provided to passengers of foreign ships and aircraft.
Exempt from VAT:
- universal postal services;
- medical services related to the use of blood and its components, the provision of breast milk, as well as transplantation of human organs and tissues;
- services of professional dentists;
- work of social services organized by the municipality;
- basic vocational, secondary and higher education;
- transportation of sick, injured and disabled people;
- insurance services;
- rental and leasing of real estate;
- sale of lottery tickets and organization of gambling;
- turnover of investment gold.
Mandatory registration as a VAT payer is provided for business entities whose taxable turnover at the beginning of the calendar year exceeded the mark of 40,000 euros.
A foreign company selling goods or services to an Estonian consumer remotely is not required to pay or report VAT. An exception is provided only for those who sell excisable products. In this case, tax representatives assume the responsibility for transferring the fiscal liability.
Social contributions
Main taxes in Estonia in 2021:
- corporate income tax – 0%;
- sales tax (VAT) – 20%;
- social tax rate - 33%;
- income tax rate with withholding – 20%;
- income tax on dividends – rate 20/80;
- unemployment tax (employee) – 1.6%;
- unemployment tax (employer) – 0.8%;
- 2nd pillar pension fund – 2%;
- the amount of income not subject to income tax from January 1, 2021 – 500 euros/month;
- the minimum salary from January 1, 2021 is 500 euros gross (or 2.97 euros per hour);
- tax-free daily allowance for a foreign business trip - 50 euros for the first 15 days and 32 euros each subsequent day.
For employees, the unemployment insurance premium is 1.6% of their salary. Non-resident workers are exempt from it.
Pension contributions for Estonian residents are set at 2% of monthly earnings.
Rules for taxation of profits of organizations
One of the most attractive factors of doing business in Estonia is that the profits of companies operating in the country are taxed upon distribution. This means that the company pays income tax in Estonia not on accrued amounts derived from accounting data, but on dividends paid to co-founders.
The tax rate is determined in the Law “On Income Tax”. From January 1, 2021, its size was reduced from 20% (or 20/80 of the net amount) to 14% (or 14/86 of the net amount paid), provided that dividends are paid on a regular basis for at least 3 years in a row .
In practice, the legislator suggests using the following scheme:
- in 2021, a rate of 14% will apply to an amount equal to 1/3 paid in 2021, the balance being taxed at a rate of 20/80;
- in 2021, this limit will be increased to 1/3 of the total amount paid in 2021 and 2021;
- a full transition to a reduced rate is possible from 2021 (however, the amount of payments should not exceed the average for the last 3 years).
The responsibility for withholding and transferring tax to the budget rests with the source – the company paying the funds. Part of the company's profit that is received in the form of dividends from participation in another business is exempt from taxation.
The country also does not have a separate capital gains tax. All transactions involving the disposal of valuable property or intangible assets, as a result of which the former owner received a financial benefit, are regarded as standard sales for corporate profit.
The positive result of the transaction is taxed according to the rules of the Law “On Income Tax” (in terms of distribution of dividends).
Land tax
Estonia has a mandatory land tax that all land owners must pay. However, a certain list of benefits is provided - both depending on the identity of the payer (for example, pensioners), and depending on the type and purpose of the land plot.
Information for owners of apartments and houses
There is no real estate tax in Estonia if a person intends to buy an apartment, house or plot.
The future owner of the home will only have to pay notary services in the amount of 150 euros and a state fee for entering the apartment or house into the register. The rate depends on the price of the real estate, the minimum is six euros.
If individuals purchase country real estate for the purpose of investment, they will need to obtain permission from local authorities. The price of such a certificate is 150 euros.
The land tax rate for an apartment is 30 euros/12 months. In the north-eastern part of the country, most 1-3-room apartments fall under this rule.
Estonia has specific procedures and state fees that are not provided for in other countries.
Persons who build a house and erect a fence have to pay a fee for it, its amount is 35 euros.
Information for car owners
On 12/05/2016, the Estonian Ministry of Finance made a decision regarding a new duty for car owners.
Today, deductions are collected only upon the initial registration of a vehicle in the country. Tax must also be paid when the owner of the car changes.
The tax rate is linked to carbon emissions. If such an indicator is absent, then the engine power is taken into account. It is expressed in kilowatts.
The rates for taxable cars are presented in the table.
| Carbon dioxide emission rate (g/km) | Motor power (kW) | Fee amount (euros) |
| 92–100 | 77–84 | 59 |
| 162–161 | 125–132 | 303 |
| 292–301 | 244–251 | 579 |
For emissions above 301 g/km, two euros are added for each additional gram of carbon dioxide.
Estonian tax officials claim that trucks weighing more than 3,500 kg, as well as tractors and buses are exempt from contributions to the state treasury.
In accordance with the Convention for the Prevention of Double Taxation, when exporting a vehicle to another EU country, the taxpayer may qualify for a duty refund.
This is possible if the carbon tax in Estonia is higher than in another EU country.
The car owner can also apply for a refund of the duty when disposing of the vehicle.
Excise taxes
In the state, tax legislation establishes a fairly wide list of excise taxes that are charged on various types of goods, primarily alcoholic beverages, tobacco products, fuel (fuels), motor vehicles, and so on. When calculating excise duty, a large number of nuances are taken into account, including whether a certain product was produced on Estonian territory, whether local packaging is used to package imported raw materials (for example, imported alcohol), and so on.
Excise rates for various types of products are periodically reviewed, and in connection with this, appropriate changes are made to the current legislation.
Other obligations
Unlike most European countries, Estonia does not levy a property tax. However, when making transactions for the purchase or alienation of property, you will have to pay stamp duty in the amount of up to 0.04% of the transaction amount. Formally, the budget is replenished only by those real estate owners who own land plots.
Land tax is required to be paid by owners, permanent users and developers of the territories allocated to them. Obligation rates are approved at the municipal level and range from 0.1–2.5% of the land tax value (current for 2021, broken down by region, can be found on the Tax Department website).
Only the part of the plot located under a residential building (from 0.15 to 2 hectares) is exempt from taxation. But only on condition that this building is the place of official registration of the owner of the land. The basis for levying a fiscal liability is in Estonia.
Some obligations apply only in certain territories. For example, Tallinn advertising fee. From 2021, it is calculated daily at the rate of 0.55 euros per square meter of advertising space per day. Payment is made in advance, on the first day of the selected reporting period; at the discretion of the payer, this can be a week, month, quarter or year.
In addition, local administrations can set their own fees:
- for the use and pollution of the environment;
- to close roads and streets;
- for a motor vehicle;
- for entertainment;
- for keeping animals;
- for parking.
Important nuances
For legal entities, the tax year lasts 30 days. Tax reports in Estonia must be submitted every month in 2021.
Documentation is submitted by the 10th day of the month following the reporting period. If the taxpayer is not registered in a special register, then he should submit a declaration upon completion of the procedure for redistributing profits.
I suggest watching the video “New taxes in Estonia”
For each day of delay, a fine is charged, its amount is 0.06% of the amount indicated in the form.
Salaries in Estonia
In 2021, salaries in Estonia will continue to increase. At least that’s what the official press services of the state say. The current minimum wage is 540 €. In the hourly version – 2-78 € per hour.
Compared to the year before last, the average Estonian began to receive 7.6% more. Approximately the same trend was observed last year. Analysts note that even earlier (2014) the growth rate was at 6%.
Cities of Estonia on the country map
Despite the positive aspects in the economic development of the state, many Estonians prefer to look for work in other EU countries. This has led to a shortage of specialists in many areas, not to mention low-paid specialties that do not require qualifications.
Estonian salaries
If the minimum leaves much to be desired, the average salary in Estonia has reached a fairly favorable level. 6-90 € per hour. This is below the level of developed European countries, but much higher than in the CIS countries neighboring the Baltic states.
Last year's level: €1,146. But if we consider the last month, December, as a starting point, it comes out to 1,248 €.
Growth was noted in all budgetary and industrial sectors. Some areas of activity are ahead of others. Administrative and support activities are especially progressive in terms of increasing employee income. Here the increase turned out to be higher than the general for the country 7.6% by 8.8%. In second place are real estate companies. In them, wage growth was 14.3%.

An increase in wages above the statistical average was also noted in the following areas in 2021:
- medicine;
- education;
- forestry;
- fishing;
- Agriculture;
- catering business;
- connection;
- information;
- social care;
- hotel business.
In all of the listed areas of activity over the past year, salaries increased by more than 7.6%.
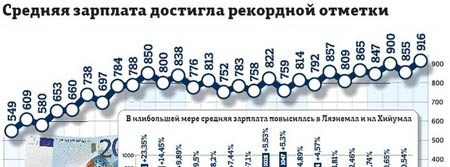
In Estonia in 2021, as in previous years, the leading positions in terms of employee salaries are occupied by the financial sector and communications.
The level of income of the population in the country depends on the region. In last place today are the counties of Jõgeva County, Saare County and Põlva County, where the average did not exceed €884 (gross). The first places were taken by the counties of Tartu County and Harju County – 1,149 € and 1,271 € respectively.
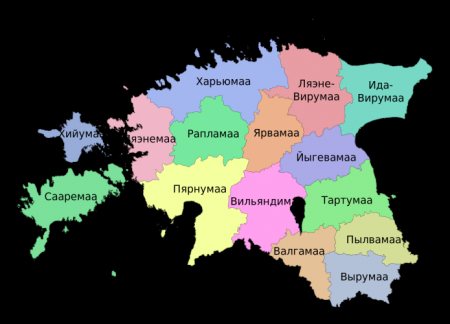
Administrative map of Estonia
Statistical studies of the issue also noted that the level of employment has also undergone changes in various regions and segments. New workers have been added to the scientific and healthcare sectors. More people are employed in finance and insurance. The demand for social security and technical workers has increased.
Meanwhile, full unit reductions have been made in some areas of activity. These are mining and real estate. Many people work part-time in other services.
Taxes in Estonia
When talking about what the minimum wage in Estonia is and its average in various areas and regions, one should always take into account that we mean the gross indicator, that is, without taking into account what citizens pay into the state treasury.

The following fees are deducted from the salaries of officially employed residents and non-residents of the country:
- Income tax in Estonia. For 2021 its size is 20%. The minimum salary of 180 € is not subject to this tax.
- Unemployment insurance amounting to 1.6% of salary.
- Contributions to pension accumulation are 2%.
As a result, if we take the average salary for Harju County as 1,149 €, after deductions the employee is left with a net amount of 912-92 € . Most of all - 183-23 - is taken by income tax.
Watch the video about taxes and business in Estonia.
Salaries of workers in various fields
Of the popular vacancies available not only to residents of Estonia, but also to visitors, the most paid positions are in the IT field. A qualified programmer earns a gross of about 2,000 € per month. Truck drivers, no less in demand in the Baltic state, lag behind in salaries by as much as 400 €. They are paid this year 1,600 €, which in net amounts to 1257-12.
The salary of a teacher in Estonia, if we talk about averages, is 1500 €, and the minimum is 1250 €. This is higher than sales professionals (approximately 1,200) and chefs (1,144). The average salesperson in Estonia earns 1000 €, a auxiliary worker – 978 €, a seamstress – 959 €.
Despite the fact that wages are rising, those who work in low-paid jobs will not notice much change, as the average growth rate - 7.6% - has dropped to 1-2% in some areas.

Employment of foreign citizens
From the point of view of Russians and representatives of other CIS countries, Estonia is considered a favorable state for living and working. Its climate and culture are comfortable for residents of the former Soviet Union, and its economic level, which is an order of magnitude higher, allows you to expand your comfort zone and think about new prospects. Another favorable factor is the large percentage (25%) of the Russian-speaking population.
Finding a job in Estonia is not difficult, since 30% of job offers are located on the Internet. You can find a job at home, and then, having completed the necessary documents, come to Estonia.
The leading sectors in the job market are IT, medicine, heavy-duty cargo transportation, construction, education, etc. You can easily find both a job with high qualification requirements and one that does not require experience or education.
In order to obtain a position as a salesperson, laborer, seasonal worker, etc. It is not necessary to speak Estonian. People who do not speak Estonian can also be invited to jobs with qualifications such as programmer, but they need to know English.

Legal employment under a contract in Estonia means that you will be protected by law, have the right to work and rest, and receive all the necessary social guarantees. Estonians work on a five-day system. Weekly employment – 40 hours (8 hours per day).
Estonian work visa
In order to engage in work in Estonia, you need to apply for a category D visa. With it you can stay in the state for a maximum of one year. This type of permit does not give the right to travel to other countries of the European Union.
A visa is issued at the embassy. The following documents must be submitted:
- international passport. Its duration must exceed the visa expiration date by at least 3 months;
- one color photo measuring 3.5x4.5 cm, made on high-quality matte paper. The background of the image is light;
- visa application form, which must be filled out and personally signed by the visa applicant (here);
- health insurance policy covering medical expenses in the amount of €30,000;
- a letter drawn up by the employer stating that the citizen has been hired for a certain vacancy;
- certificate of employment, if any, drawn up according to the international standard, indicating length of service, salary, position, etc. (the template in Russian can be downloaded here, in English here);
- a written explanation of the purpose of the trip;
- receipt of payment of the consular fee;
- booking transport tickets;
- hotel reservation, etc.
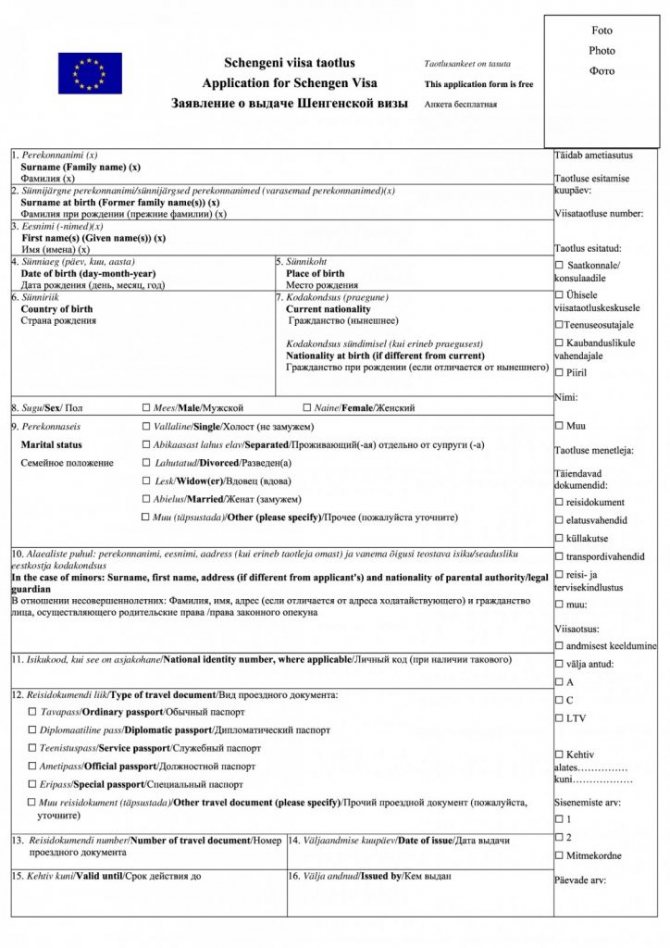
Application form for a visa to Estonia, 1 page.
Instead of a certificate of employment, students should present a document from the educational institution stating that they are currently studying. Pensioners must present a pension certificate.
When submitting documents to the Consulate, you should always take into account that they may request additional information.
It is possible to extend a category D permit for another 90 days if necessary..
Work permit in Estonia
If employment is expected for a period of more than six months, the employer must take care of obtaining a work permit for a labor emigrant. To do this, a request is submitted to the border guard and police. The document lists all the details about the vacancy.
Often, the need to obtain the right to work becomes an obstacle to inviting outside specialists. Employers take this step only when they cannot find specialists of the appropriate level in Estonia.
It is not recommended to take a job in Estonia illegally. In case of a single violation of migration legislation, the violator will be subject to a fine of 600 to 1,700 €. A repeated violation may result in deportation from the country and an entry ban for up to 10 years.
Employers for providing work to illegal immigrants in 2021 will be punished with a fine of 1,500 €. For repeated violations, they face a prison sentence of up to 3 years.
About the experience of working in Estonia - in the video.
Basic requirements for foreign workers
Despite the fact that Estonia is a former member of the USSR, a Russian-speaking candidate will only receive an invitation to an interview if the following requirements are met.
- Language skills. Ideally, a potential mercenary should be able to speak Estonian. But when applying for a job in an international organization, it is enough to know English and Russian.
- Availability of qualifications. The applicant is required to provide a diploma of higher education, all available certificates, and confirm their knowledge in practice. Candidates for a creative position, in addition to the listed documents, must provide a portfolio of work.
- Monthly income amount. To obtain a residence permit, the level of future salary should not be less than the average annual rate (by local standards).
Official employment of foreigners
For citizens of the Russian Federation and CIS countries, Estonia is a favorable place to live and work. The climate of this country is quite comfortable for residents of the collapsed Union, and the economic situation in the country allows one to significantly expand the zone of personal comfort.
In the country, 25% of the population speaks Russian fluently. Finding a job is absolutely no problem since it can be done online before moving to Estonia.
You can easily find vacancies in areas such as:
- the field of information technology;
- medicine;
- freight transportation;
- education;
- construction.
A foreigner will be able to find work both in areas where special education is needed, and in areas where training and experience do not matter. In many areas you can get hired without knowing the language. One of the most promising jobs is to work as a programmer.
With legal employment, a foreign citizen will be protected by the legislation of the country, have the right to a work schedule and proper rest, and also enjoy all social guarantees.
In order to officially work in Estonia, you need a work visa category D.
With this visa you can live and work in the country for one year.
Required documents
In order for a Russian to find a job in Estonia, he needs a category “D” visa valid for up to 1 year. List of documents to be submitted to the consulate:
- international passport;
- color photo 3.5 x 4.5 (European standard);
- A completed application form;
- letter of invitation from the organization;
- medical insurance (coverage amount of at least 30,000 EUR);
- a written explanation of the purpose of the visit from the applicant;
- bank statement confirming the availability of sufficient funds;
- a check confirming payment of the state duty;
- certificate from the last place of work (position, salary for the past six months);
- confirmation of the availability of a place of residence (hotel, rented house/apartment, etc.);
- photocopies of two-way tickets.
This list is not exhaustive. In some cases, the applicant may be required to provide additional documentation.
Work permit
This paper is issued by the Police Department. It must contain in detail all information regarding the migrant’s employment.
You do not need to obtain a permit if the contract is drawn up for a period not exceeding 180 days. Also, execution of the document is not necessary for those who are EU citizens, holders of an Estonian residence permit or permanent residence permit.
Employer Responsibilities
The organization hiring a migrant must pay him for his work in accordance with the indicators of the previous year. The level of income of a mercenary depends, in particular, on how in demand his qualifications are and whether he has an academic degree.
The work of nannies and caregivers, experts, analysts and seasonal workers is paid according to a similar principle in Estonia.
Penalties for illegal employment
Unofficially working migrants can become a real burden for a company. For violating Estonian legislation, the organization must pay a fine of 1,500 euros. Repeatedly providing a position to an illegal immigrant (more than 2 times a year) threatens the employer with imprisonment for up to 3 years.
Working illegal immigrants also bear partial responsibility for their actions. An employee who works illegally is subject to a fine of 600 to 1,700 euros. If a detained person has been “caught” doing illegal work more than once, he will be deported and banned from entering Estonia for up to 10 years.
Sources
- https://migrantvisa.ru/zarplata/srednjaja-zarplata-v-jestonii/
- https://emigrating.ru/uroven-zhizni-v-estonii-osobennosti-prozhivaniya-v-strane-zarplaty-meditsinskie-uslugi-i-obrazovanie/
- https://emigrating.ru/zarplata-v-estonii/
- https://hochusvalit.com/estoniya/vostrebovannye-professii-v-estonii
- https://ostrovrusa.ru/srednyaya-zarplata-v-estonii
- https://zagranportal.ru/estoniya/finansy-estoniya/nalogi-v-estonii.html
- https://prifinance.com/nalogooblozhenie/nalogi-v-estonii/
- https://migrant-fms.ru/evropa/estoniya/nalogi-v-estonii/
- https://lenovoz.ru/estoniya/trudoustroystvo-i-zarplata
- https://HRMonitor.ru/world/eu/zarplata-v-estonii.html
Employment and salaries for foreigners
Labor tourism in Estonia is directly proportional to the outflow of indigenous people who go to work in more solvent EU countries.
More than a third of the vacancies are posted on the Internet and anyone can try to find a niche in developing industries. Mainly required are information technology specialists, medical personnel, builders and teachers. The level of qualifications often does not matter, but it is worth remembering that without knowledge of English and minimum work experience, wages will be 25-30% lower.
To find employment in Estonia, Russian citizens must submit an application to the consulate for a residence permit. The issue will be resolved within 2 months. Then you need to apply for a work visa.
The average salary of a hired employee with legal employment is up to 2,000 euros per month, depending on the type of activity. For violations of the law, foreign citizens are punished with fines, and for repeat violations - with imprisonment.
It became known what the average gross salary in Estonia is
Official reports of rapid wage growth come amid cautious forecasts for the future of the national economy by economists and trade union pickets demanding higher wages.
TALLINN, August 28 – Sputnik. In the second quarter of 2020, the average monthly gross salary was 1,419 euros per month, an increase of 7.4% over the year, and by 5.9% compared to the first quarter of this year.
It is noted that the highest salaries were in the information and communications sector (2,390 euros), in the financial and insurance sectors (2,296 euros) and in the energy sector (1,913 euros).

An increase in wages was recorded in all types of activities, with the exception of two - in agriculture and real estate.
The average monthly accrued wages in April was 1,411 euros, in May - 1,400 euros and in June - 1,445 euros. It is also reported that the average gross hourly wage has also increased sharply over the year.
Now it is 8.22 euros, which is 9% higher than in 2018.
At the same time, the growth of real wages (the dependence of average wages on inflation) turned out to be lower - 4.4% per year.










