Open borders
South Korea and Russia entered into an agreement on the mutual abolition of visas back in 2014. In the East Asian republic, this led to an increase in the number of Russian tourists. Official Seoul hopes that in 2019 the number of travelers from the Russian Federation will reach 370 thousand.
South Korean borders are open to many of our compatriots. The following can count on free entry:
- tourists;
- persons arriving for private purposes (visiting friends and relatives, business negotiations, etc.);
- transit passengers.
However, they do not have the right to:
- enter educational institutions;
- work.
Illegal labor activity is fraught with deportation and a ban on entry into the country for at least 5 years.
Types of visas to South Korea
In cases of short-term stay in the Republic of Korea, a citizen of the Russian Federation does not need a visa, but the applicant can receive one of 34 types of visas, which in turn are divided into subtypes, depending on the duration and purpose of stay in the country.
Types of visas and their brief descriptions are presented in the table.
| Types of visas | Short description |
| S-3 – tourist | short-term tourist, valid for no more than 90 days. There are 9 subspecies. For example, visa permit C-3-3 is issued by persons who plan to undergo treatment in the Republic of Kazakhstan, and C-3-2 is issued by travelers visiting the country as part of a tourist group. |
| D-2, D-4 – educational | Issued for a period of 6 months to 2 years. Will be needed for studying in Korean schools, colleges, universities, and for learning a foreign language |
| D-8 – business visa | Issued by a foreigner who is the head of a Korean corporation with foreign investment or plans to engage in entrepreneurial activity. Issued for a period of 2 to 5 years |
| H-2 – work visa | Designed for ethnic Koreans up to the third generation. Valid for 3 years. Gives you the right to work. Subject to official employment, extended to 2 years |
| F-4 – visa for so-called overseas Koreans | This status is given to ethnic Koreans of three generations who have citizenship of the Russian Federation and other countries of the former USSR. This Korean visa is issued for 5 years and does not set restrictions on the period of stay in the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| F-5 | Issued by persons entitled to obtain a residence permit |
| F-1 – family visa (escort visa) | Designed for foreigners who travel to the Republic of Kazakhstan with relatives or accompany foreign diplomats, public figures, and for housekeepers. Issued for a period of up to 2 years. |
| F-6 – marriage | Can be opened to the spouse of a South Korean citizen |
| E-1, E-2, E-3, E-5, E-6 – professional work visas | Issued to those who plan to work, engage in teaching activities, or conduct research. The peculiarity of this type of visa is that if a foreigner is fired, it is necessarily canceled |
| G-1 – visa for multiple purposes | Issued, for example, to persons who have applied for refugee status or are participating in legal proceedings in the Republic of Kazakhstan. Validity period – 1 year |
Visa-free stay
The visa-free regime is limited not only by the purpose of visiting the state, but also by the time of residence. Staying in the republic without a visa is allowed for no longer than 2 months, with the possibility of re-entry for another month. But in total, South Korea is allowed to stay for a maximum of 3 months in one half-year.
Note! At South Korean airports and seaports, foreign visitors are fingerprinted and identified by facial pattern. Children and teenagers under 18 are exempt from biometric control.
Visa-free regime and its features
In 2014, an agreement was concluded between Russia and South Korea on the mutual abolition of visas. However, this does not mean that Russians are now allowed visa-free entry into South Korea for an unlimited time.
Russian citizens can visit South Korea without a visa subject to the following conditions:
- the purpose of the trip is tourism, private trips (visiting friends or relatives), business trips (for example, negotiations) or transit;
- the period of stay of the country does not exceed 90 days within 180 days;
- the period of stay in the country within one trip cannot exceed 60 days.
When entering South Korea you must have:
- international passport;
- ticket for a return flight or a flight to a third country;
- confirmation of hotel reservation or confirmation of the inviting party;
- migration card (can be filled out on the plane);
- customs declaration (can be filled out on the plane);
- confirmation of availability of funds for the period of stay;
- medical insurance policy.
At the border you will be asked to undergo fingerprinting procedures, as well as facial photography.
Persons who entered South Korea on a visa-free basis are prohibited from employment and study. If you are traveling to South Korea for these purposes or plan to stay in the country for more than two months, you must first obtain a visa.
Subtleties of entry
When traveling to an Asian country on a visa-free basis, you must have with you:
- A foreign passport that will be valid for at least six months upon the foreigner’s return to his homeland.
- Migration card. Forms are distributed on the aircraft to be completed during the flight.
- Customs declaration. The form must be completed on the plane or at baggage claim.
- Tourist voucher, hotel reservation or coordinates of your place of residence.
- Return ticket, and during transit - tickets and visa to a third country.
- Cash guarantees for the entire trip.
- Letters of guarantee and contacts of receiving organizations or individuals.
- Medical insurance policy (it is recommended to take out).
Formally, only a foreign passport, migration card and declaration are mandatory documents submitted upon arrival. However, to establish the reason for the visit, the citizen may be required to submit other of the above papers. If the guest does not fully prove the purpose of the trip, he will be denied entry. The tourist will be sent back on the next flight of the airline he arrived with.
South Korea without a visa - conditions of entry and stay for Russians
Not all Russian citizens can use the visa-free regime. The agreement between the countries clearly defines the categories of foreigners who have the right to visit Seoul and other South Korean cities. Unimpeded entry is available:
- Tourists.
- Private visitors are people who want to visit their relatives, friends, and conduct business negotiations.
- Transit travelers.
They are prohibited from enrolling in universities or colleges, working, or conducting illegal activities while in South Korea.
At airports and seaports, all Russian citizens are required to submit fingerprints and undergo facial recognition. Children and adolescents under 18 years of age are exempt from this procedure.
How long can you stay in the country without a visa?
Russians can stay in South Korea for no more than two months. It is allowed to extend your stay by a month after this period has expired, but only once. For six months, Russian citizens are allowed to live in the country for no more than three months.
Passport requirements
Entry is permitted only with a foreign passport. The document must be valid for another six months or more after the Russian citizen returns home.
What other documents will you be asked to present at the border?
In addition to the passport, foreigners are required to show the border guards other documents:
- Migration card. Forms are given to all passengers on the plane and they explain how to fill out each line. The migration card must be completely filled out before the plane lands at one of the airports in South Korea.
- Customs declaration. You can also fill it out on the plane or in the baggage claim area.
- Tourist voucher, hotel reservation or rental agreement for an apartment, house or apartment at your place of residence in South Korea.
- Return ticket. If a tourist from Russia transits through South Korean territory, then he must present a visa to another country and plane tickets.
- Cash guarantees that will confirm the foreigner’s ability to provide for himself for the entire period of his stay in South Korea.
- Contacts of the host party, individuals, organizations.
- Letters of guarantee.
- A health insurance policy is not included in the list of mandatory documents that will be required at the border, but take care of your own health.
By the way, you can take out an insurance policy without leaving your home. The online service will compare offers from the most popular insurance companies for you, and you will be able to choose the one that suits you.
The migration card contains personal information about the passenger, his address of residence in South Korea, and foreign passport data. Data must be entered correctly and no blots or mistakes must be made.

A customs declaration is a small form where you need to make marks next to the questions. Passengers indicate that they do not carry animals, plants, goods intended for sale, weapons, drugs, or large sums of money. For transportation to South Korea, no more than 100 thousand US dollars or the equivalent is 100 thousand Korean won.
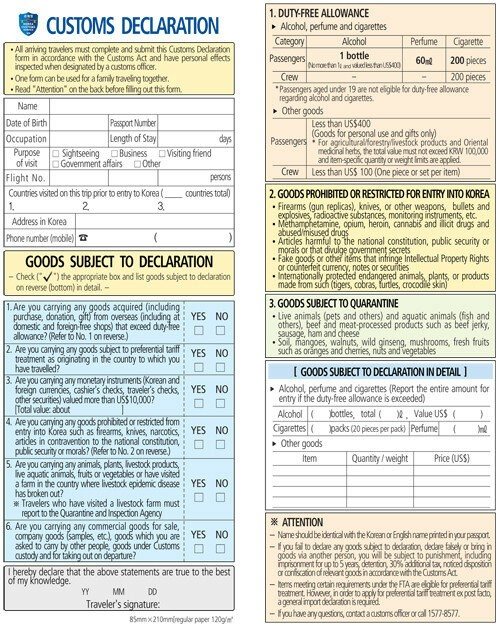
Border guards have the right to demand from a foreigner other documents that confirm the purpose of the trip. If such papers are not on hand, entry will be prohibited. A foreigner will not be able to stay at the airport for long. He will be sent home on the closest airline flight on which the tourist arrived in South Korea.
The final decision on whether or not to allow Russians into the country is made by representatives of the border authorities. When leaving the plane, foreigners are advised to have on hand the documents that are asked for at the checkpoint. All questions asked must be answered calmly and clearly, without showing uncertainty or nervousness.
Documents for children
The child is subject to all the rules and regulations of the visa-free regime, which also applies to adults. You can enter the country with children if you have the following documents:
- Birth certificate.
- Power of attorney from parents or guardians. The document must be certified by a notary so that there are no difficulties at the border.
- Your own foreign passport, if you have one.
- Permission from the other parent or guardian to take the child outside the Russian Federation.
Important nuance
So, in practice, the bilateral agreement between Seoul and Moscow does not mean unhindered visits to the East Asian republic for Russians. The visa-free regime facilitates, but does not guarantee one hundred percent, travel to Korean territory. The final decision on tourist admission is made by representatives of the border authorities. To make a favorable impression on the border service, it is recommended:
- keep on hand documents that may be needed at the checkpoint;
- calmly and clearly answer all questions.
Registration procedure
How to obtain a South Korean entry document? Applying for a visa to South Korea begins with filling out an application form and collecting a package of documents. The list of documents to be submitted depends on the type of visa required. A set of documentation must be brought to one of the Korean diplomatic missions:
- embassy in the capital of the Russian Federation;
- consulates in Irkutsk, Vladivostok, St. Petersburg.
An applicant can apply for a visa to South Korea personally or through an intermediary. A power of attorney is not required. It is also possible to obtain a visa stamped in your passport through an intermediary. The Korean Embassy does not consider applications sent by mail.
It is important to know! Those who have their application rejected always have the opportunity to try again. Applications for visas to South Korea can be submitted an unlimited number of times. Please remember that visa fees charged for processing the application are non-refundable.
Prices for attractions
In Seoul you can see almost everything for free or inexpensively. Many museums in South Korea are free or require a nominal entrance fee. For example, a ticket to the Royal Palace costs only ₩3k. But the prices for entrance to amusement parks and observation decks are sky-high, see below for yourself.
What to see in Seoul for free:
- Dongdaemun Design Plaza - Zaha Hadid building
- Bukchon Hanok Village with traditional houses
- Changing of the guard at Gyeongbokgung Royal Palace at 10:00 and 14:00
- N-Seoul Tower Outdoor Terrace and Park
- Namsangol Village - Open Air Museum
- Cheonggyecheon Park - a stream park on the site of a former highway
- Rainbow Bridge (Banpo Bridge)
- Beautiful hall with plants in Seoul City Hall (Seoul City Hall)
- Jeongdong Observation Hall on the 13th floor of the Seosomun Building
- Seoullo 7017 is a park on the site of the former overpass above Seoul Station. The views are stunning!
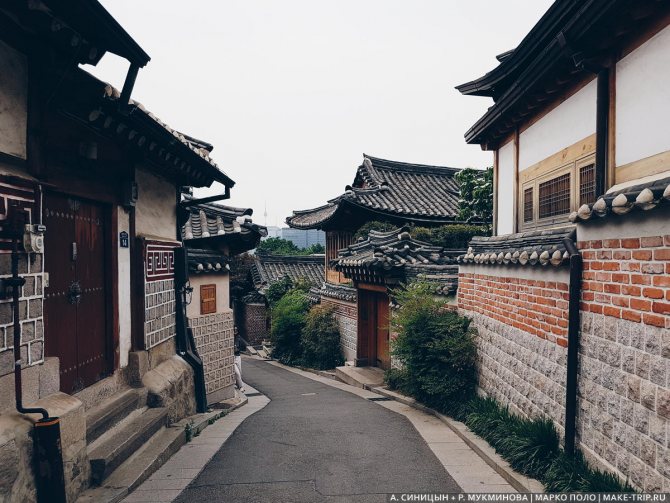

Bukchon Hanok Village with traditional houses.
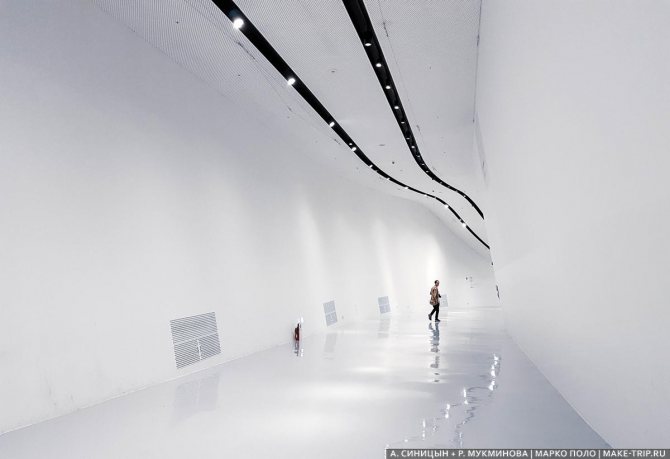

Dongdaemun Design Plaza - Zaha Hadid building.

The views are stunning! Prices for attractions and entertainment in Seoul:
- Exhibitions at Dongdaemun Design Plaza - about 10k ₩.
- Entrance to the royal palaces - 3k ₩ each (museums on the palace grounds are included). You can buy a combo ticket for 10k ₩.
- N-Seoul Observation Tower - 10k ₩.
- Everland Amusement Park - 87k ₩ for 2 days, for 1 day (day) - 56k ₩.
- Lotte World Amusement Park - 54k-57k ₩. If you take the Magic Pass for 100 thousand won, you won't have to stand in line.
- Seoul Sky Observatory at Lotte World - 25.5k-35k ₩.
- Aquarium at Lotte World - 16.5k ₩.
The experience of Marco Polo. We spent only 16k ₩ on sightseeing for two of us - we went to Gyeongbokgung and to an exhibition of Korean painters.

- How much does a trip to Singapore cost?
- How much does a trip to Japan cost?
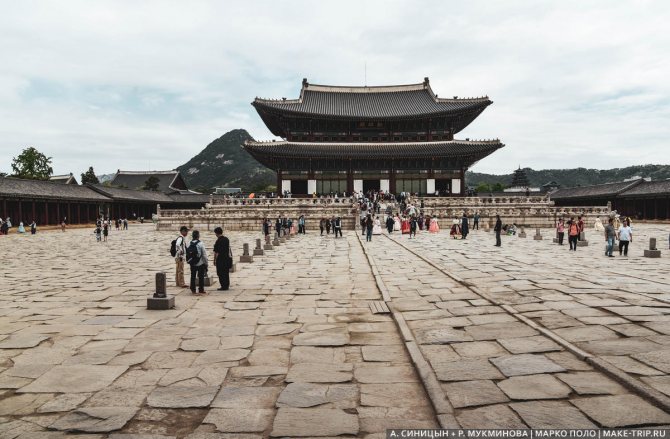

Gyeongbokgung Royal Palace in Seoul.
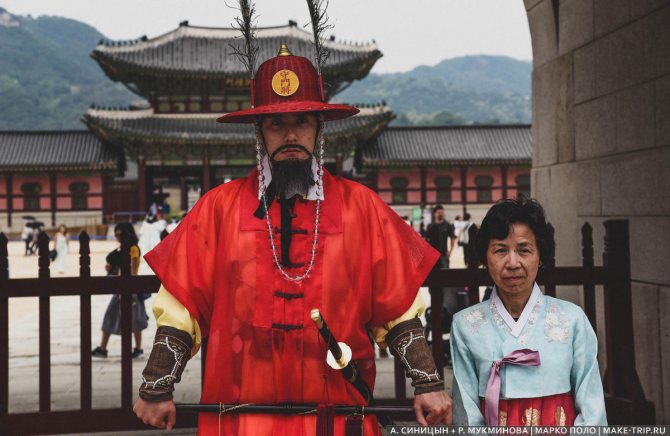

Guard of Gyeongbokgung Palace in Seoul. The Changing of the Guard can be viewed for free at 10:00 and 14:00.
Main types of visas
You cannot get a visa to Korea for free. Consular fees are collected from all candidates. The fee is paid in cash in US dollars. How much a visa costs depends on its type.
| Main categories of visa to Korea | Peculiarities | Visa cost |
| Visa C | Is a one-time document Validity period for the document and permissible stay - 3 months Opens to: tourists, people visiting relatives, businessmen, patients of Korean clinics, actors, musicians (short-term employment), journalists | $50 |
| Working | Visa validity period - from 3 months Issued only upon request of the future employer at the Korean Migration Office. If the answer is yes, a special certification number will be provided upon request. On its basis you can obtain a visa. Highly qualified specialists can apply for the document | $80–120 (price depends on how long the foreigner was invited to work) |
| Student | Designed for students from both certified and non-certified universities | $80 |
| For ethnic Koreans | Validity period of the document - 5 years Duration of permitted stay in the republic - 2 years continuously Issued to Russian Koreans up to the third generation, taking into account those who were born and/or lived in the Soviet Union before 08/15/1945 (they are considered the first generation) Opens without age limits This visa allows employment in a number of fields (the list of industries may change every year) | $120 |
| For minor children, husbands and wives of ethnic Koreans | Is multi-use Shelf life – 1 year Permitted stay – 2 months | $120 |
| For adult children of ethnic Koreans (fourth generation) | Multiple-entry visa Validity period of the document – 5 years Duration of permitted stay – 3 months every six months | $120 |
Main visa categories
It is natural that the type of visa directly depends on the purpose of the planned trip.
Short stay visa (C)
The permissible period of stay in the country is 3 months. This type of visa is issued in a number of cases:
- tourist voyage, guest visit, cultural and business non-commercial activity - type C1;
- resolving any issues related to business: negotiations, market research, conclusion of transactions - C2 business visa;
- business trip of an employee of any type of media for short-term journalistic work – C1.
Working (C, F)
Issued to certain categories of citizens:
- highly qualified specialists needed by the employer;
- ethnic Koreans (F4);
- for creative people for short-term work (artists, musicians) – C4.
Student (D)
For all international students in South Korea, including non-certified educational institutions. The list of certified universities can be found here.
For ethnic Koreans (F)
A special type of visa for fellow citizens who live in other countries. For Koreans currently living in Russia, as well as those who were born or lived in the USSR before August 15, 1945 - F4 visa. Holders of such a visa are allowed to visit the country, study, and work for 5 years, with a maximum period of 2 years for each entry.
Researcher Visa (E)
Intended for professors and scientists to conduct research useful for the Republic of Korea.
Basic visa documentation
To obtain a South Korean visa, you need to collect certain documents. Their complete list depends on the type of entry paper requested. Some of the documentation is the same for all applicants. Those wishing to visit the country with a visa must submit the following documents for a visa to Korea:
- Completed and signed application form. The forms are available on the embassy’s website. Information on the form must be entered in Korean or English.
- Photo 35 by 45 mm, taken maximum six months ago. Only color photographs are accepted.
- A foreign passport valid for at least six months by the time the visa expires.
- Receipt for fees paid.
Seven rounds of checks: how to fly to South Korea in the midst of a pandemic
It is now difficult to imagine that people once traveled freely around the world simply because they were tourists. Many countries were ready to receive guests. Russians wishing to visit South Korea could stay in the state without a visa for as long as 60 days.
South Korea has opened its borders to Russians since October last year, but there is no talk of a return to everyday tourism. Strict quarantine measures continue to apply to everyone wishing to visit the country.
Before the start of the pandemic, I lived and studied in China, but now it is not so easy for students to get into China; they are not invited to the country. I really wanted to return to Asia again. The idea to go to study in South Korea came when Seoul restored air traffic with Russia.
I called the consulate and found out that entry is now open for students and visas are being issued. After that, I found the University of Language Courses in Seoul and entered there; after a month and a half I was already in Korea.
I had to buy a ticket with a transfer in Turkey - it was cheaper. There are also direct flights operated by.
A negative COVID-19 test was required for the flight. I made it at Vnukovo airport. The results were ready within two hours after taking the tests, and I went to check in for the flight with my head held high. At the counter they asked me for all documents related to my studies and specified where I would be quarantined.
On the plane we were asked to fill out four forms. I once again talked about the purposes of visiting Korea, where I will be quarantined, who will be my caregiver, and whether I am bringing fruits and meat with me.
Upon arrival in Korea, seven stages of verification awaited me, which took about three hours.
Stage 1. Temperature measurement, viewing a negative test, issuing papers for the next test.
Stage 2. Installing a self-isolation application.
Stage 3. Filling out the data in this application, viewing the address by specialists. Checking my visa and other documents.
Stage 4 I called the university director and confirmed that I really plan to study at this institution.
Stage 5 Passport control. Reviewing the visa and checking the application that everything was done correctly and the address where I will be self-isolating is also correct.
Then I was glad that this was the finish line and all that was left was to pick up my things. I received the suitcase, but there were two more stages of verification ahead.
Stage 6. Inspection of the contents of the suitcases to make sure that I did not bring prohibited goods with me.
Stage 7 Checking the address, installed application. After that, they stuck an orange circle on my coat.
Then we headed out, but leaving the airport building was not so easy. A person had to come for me to accompany me to the place of self-isolation. Having arrived at the address, I had to take the coronavirus test again within 24 hours. In this regard, I managed to spend a little time in the fresh air. This was the last chance to walk down the street before being confined to four walls for another 13 days.
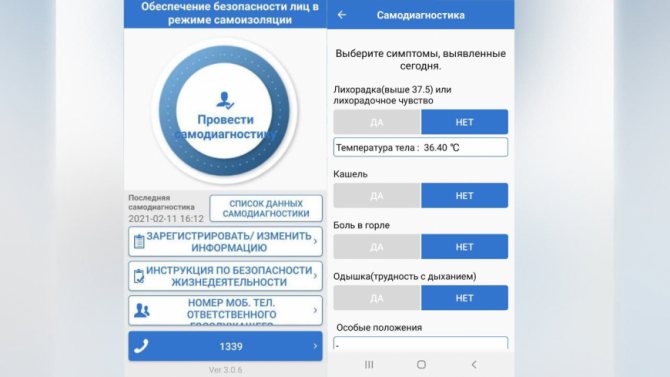
Every day, morning and evening, I entered data about my health into the application that was installed for me at the airport. If I didn't enter information on time, the app would ring like a fire alarm.
After three days in quarantine, they sent me a package from the Seoul Government: large bottles of antiseptics, a protective mask, a thermometer, hand sanitizer and even aroma sticks.
The next morning they sent me a box of food from the authorities. This food lasted me throughout the entire quarantine.
I was amazed by the care of the South Korean authorities for foreigners forced to self-isolate. After two weeks of “confinement,” I had to take the COVID-19 test again. The result, of course, turned out to be negative.
Now that everything is behind me, I can stroll through the streets of Seoul, visit beautiful places and wait for school to start.
Read also:
South Korea announces plan to build world's largest wind farm
South Korea is ready to resume cooperation with the DPRK at any time
South Korea protests Japan's claims to Dokdo Islands
Additional paperwork for visa C
For tourists
- An invitation from the host person or company. If the invitation has not been issued, you must contact an accredited travel company.
- Letter of guarantee.
For a guest visit
- Invitation from the host.
- Letter of guarantee.
- Bank statement about the account status.
- For employed people – a certificate from the employer. It must specify the applicant’s position, his salary and period of work at the enterprise.
- 2 personal income tax (if necessary).
For entrepreneurs
- An invitation from the organization and a copy of its registration.
- Letter of guarantee.
- Account statement.
- 2 personal income tax.
- Certificate from work (if available).
For people going for treatment
- An invitation from a medical institution and a copy of the clinic’s registration.
- Confirmation of consultations with a doctor.
- Employed citizens submit a certificate of employment.
- Information from the bank about the account (if the visa applicant personally pays for the treatment).
- A letter of sponsorship and a certificate of sponsor's account (if the sponsor pays the fee).
For people working in the creative field
- An invitation from an organization based in an East Asian country.
- Work permit from a Korean organization and a copy of its registration.
- Copy of the contract.
- Certificate from work in the Russian Federation.
- Letter of guarantee.
For media workers
- Invitation.
- Letter of guarantee.
- Journalist's ID.
- Referral from the editorial office where the media employee is employed.
- Certificate from work.
Additional papers for students
For those admitted to a certified institution
- Invitation from the university.
- Results of medical testing for tuberculosis.
For those admitted to a non-certified institution
- Invitation from the university with a copy of the registration of the educational institution.
- Bank statement for the amount stated in the invitation. The size of financial investments is associated with a number of factors and depends on:
- visa subcategories;
- duration of the educational course;
- location of the university (the capital or remote from the city center).
- Birth certificate (if education is paid for by parents).
- A letter from the sponsor, a certificate from work and 2 personal income taxes of the sponsor (if it is not the parents who contribute the money for studies).
- A diploma of completed education or a certificate from the current place of study.
- A copy of the interuniversity agreement (for exchange students).
- Receipt for payment for language courses (for course participants).
- Tuberculosis test results.
Additional papers for ethnic Koreans
- Passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation.
- Birth certificates:
- the candidate himself;
- mother/father of the candidate (for second and third generation applicants);
- the candidate's grandparents (for third-degree applicants). Family ties will be confirmed by a copy of the grandfather/grandmother's ID card, military ID or death certificate. The documents must record the date of birth of the ancestor.
- Marriage document (if the last name has changed).
- Tuberculosis test results.
On a note! Ethnic Koreans apply for a visa if they have originals or copies of the necessary documents certified by a notary. You are also required to photocopy all documentation (except your passport). To prove kinship, certificates from relatives of the same line must be presented.
Review of visa dossiers
Employees of the South Korean diplomatic departments scrupulously study the application form and each submitted paper. They also call the phone numbers indicated in the documents. If necessary, additional information is requested or an interview is scheduled at the diplomatic mission. If the answer is negative, the reason for the refusal can be found on the embassy website.
If the outcome of the case is positive, the visa can be obtained within 7 days. This is the average number of applications processed. With the entry document in hand, all that remains is to buy tickets to South Korea and set off on the long-awaited voyage.
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
When is the best time to go?
The best months to visit South Korea are April, May, September and October (if you plan to actively travel around the country) and from mid-June to September (if beach holidays are your priority).
In winter, you should come only if you plan to ski in the Olympic PyeongChang and the surrounding area; it is at this time that there is snow in the mountains and all the conditions for a ski holiday.
In spring the weather here is warmer than in Russia. April is famous for cherry blossoms, it looks really incredible, and May is like summer in central Russia. However, there may be a chilly wind in the evenings, so bring sweaters.

Weather in South Korea
In summer, the beach season opens from late June to early September. It's hot and humid. The ideal time for a beach holiday is at any of the many resorts, the most famous being Jeju Island and Busan.
At the end of September-October, autumn takes its toll and the trees turn yellow-red. The best time for trekking and visiting national parks, and it’s not so hot anymore.

When is the best time to go to Korea: spring and autumn










