The scale of migration processes in the world tends to constantly increase - an increasing number of people are involved in them. In search of more favorable living conditions, they constantly move from place to place, and this does not always happen within the country. Migrants who have moved for permanent residence to a foreign country must get used to its laws and rules, as well as legalize their position on its territory, while internal migrants are all familiar with this.
General concept of migration
Migration is the movement of a person either within a country or to another country. Today no one disputes the position that migration has become one of the main factors of social transformation and development in all regions of the world.
In Russia, migration processes began to be observed since 1975. It is worth noting that after the collapse of the Soviet Union they increased significantly, but by the end of the 1990s they sharply declined.
Considering the current state of affairs, it is worth saying that the migration of the Russian population in 2021 has decreased compared to the same period of the previous year. However, if we consider the picture as a whole, then some population growth in the country is still observed. It is ensured by the resettlement of foreign citizens to the Russian Federation.
Immigration to Russia in 2021 is the entry into the country of the population of a foreign state for the purpose of temporarily or permanently residing on its territory. The term “immigration” itself in this case applies to the country into which migrants enter.
Emigration in Russia, on the contrary, means leaving the country. Unfortunately, in 2021 this process has not lost its relevance. At a time when the country is ensuring population growth with foreign citizens, Russians themselves are leaving the country.
Read more about what migration processes are.
Political reasons for migration
The rapid economic growth of the last 6 years has for the first time allowed the Center for Strategic Research to formulate a long-term goal for the development of Russia. Our country has the opportunity to leave the moderately developed category, in which we have been throughout the last century, and join the group of developed ones.
More to read —> How much do they pay for the first disability group in 2021?
Historical reference
The most important factor in regulating seasonal migration is the economic situation. At the same time, it can play both the role of a pushing and attracting factor. With push-out, a person strives to go to work in any locality or country, being unable to solve the problem of earning money in his homeland.
On August 7, 2021, the Government of the Russian Federation introduced bill No. 527255-7 to the State Duma. It went through all stages of discussion, was adopted in the last - third - reading and today exists in the form of the Law “On Amendments...” dated December 27, 2021 No. 544-FZ, which comes into force on March 29, 2021.
Why does migration occur in Russia?
Various countries experience both external and internal migration. The latter most often involves relocation from villages and towns to large cities. Residents of the country are mainly interested in the reasons for the rural-urban migration of the population of Russia.
Previously, there was a trend of moving from rural areas to large cities. First of all, this was due to the improvement of living conditions in cities, as well as the lack of higher educational institutions in rural settlements and an insufficient number of jobs. Resettlement from villages contributed to the decline in the country's agricultural development. Such migration is still relevant today, but does not have the same mass scale as before. Realizing the problem of developing the agricultural industry, the Russian government decided to somehow interest the population and turn the migration process in the opposite direction. Today, those who move from the city to the countryside receive certain benefits and allowances. The state provides them with assistance in starting their own business in the field of agriculture, and also encourages employment in enterprises specializing in this area.
It is worth noting that internal migration is typical for large states, the regions of which have different climatic conditions, socio-economic development, religious foundations, and so on. Thus, the reasons for migration in Russia may be different, but most often this process is associated with the search for a better life. People move from one region of the country to another, and also move from other countries to the Russian Federation if their new place of residence opens up better prospects for them.
In order to better predict the development and scale of migration processes, it is necessary to understand the reasons for their occurrence.
Scientists working on this topic identify the following main factors influencing the migration mobility of the population:
- unfavorable political situation in the country;
- economic decline;
- bad ecology;
- interethnic disagreements;
- religious differences;
- psychological;
- interracial strife;
- humanitarian aid;
- legal reasons.
CND reform in 2021 will focus on guillotine working groups
Based on the results of government meetings on December 24, 2021, the economic picture for 2021 seemed to the government to be completely clear, definite and not causing concern. It was believed that everything had already been decided, there was nothing to argue about, just carry it out - the budget, national projects, the infrastructure investment program, “road maps” for economic deregulation; pass already developed bills, support non-resource exports, manage fuel prices to avoid inflation spikes, reduce the key rate, build apartments and issue mortgage loans, extend optical fiber to schools, distribute medicines to cancer patients, clean up the Volga riverbed.
The global economy has moved away from the crisis, but has not accelerated
Let us repeat, there were essentially no serious problems on this list. But by the fall it became clear that replacing measured and calm movement with the constant resolution of minor disputes and conflicts is something that the economy does not like. If we judge economic development by the dynamics of GDP, consumption, investment and industrial production, then based on the results of the first half of 2021, one could expect an internal conflict in power and the threat of resignation of half of the deputy prime ministers, who have been personally responsible for the implementation of national projects since May.
May 09, 2021 uristgd 116
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Standard for Electricity Consumption Per One Adygea 2021
- From what time do they sell alcohol in the Moscow region in 2021 at Dixie
- State duty details for opening a private enterprise in 2021 in Omsk
About types of migration
The concept of “migrants” has long been part of our lives and speech; in Russia in 2021, as in previous years, we don’t really think about what it means.
Migration legislation defines the meaning of the word “migrant”: this is a person who moves from one state to another for temporary or permanent residence.
However, this term applies, which many Russians most likely do not know, not only to foreign citizens permanently or temporarily residing in the country. Many will be surprised to learn that migrants can also include citizens of the Russian Federation. However, in order to clarify the situation, it is necessary to find out what types of migration are characteristic of modern Russia and what their reasons are, because first of all we are interested in the current state of affairs.
As in many other countries, in the Russian Federation one can distinguish internal and external migration. Internal, or intrastate, migration is the process of moving populations within the same country. These relocations do not go beyond the state border. An example of internal migration of the population of Russia is relocation from regions with a harsh climate to areas located further south, mass or individual relocation from villages to cities and vice versa. Citizens of a given state participate in internal migrations.
In turn, external migration in Russia during resettlement involves crossing the border. This may be entry into the Russian Federation for temporary or permanent residence, or departure of its citizens to foreign countries for a similar purpose. Internal migration does not affect the population of the country as a whole, unlike external migration, which increases it.
In addition, depending on the duration of residence of migrants in their own or foreign country, other types of migration can be distinguished, but they are of a slightly different nature.

Type: episodic
This type of migration does not have any periodicity, specific directions and specific goals. This may include business, tourist and sports trips, business trips, trips for the purpose of recreation or health, religious pilgrimages, etc. Participants in episodic migration pursue various goals and travel at any time convenient for them.
If we consider the scale of episodic migration, then it is perhaps considered the largest, but at the same time it is studied and monitored the least, except, of course, tourism. Every year there is an increase in the number of Russians traveling abroad for tourism purposes.
Type: pendulum
Commutative migration represents daily or weekly trips of a person from his place of residence to his place of work (and back), located in different localities. Participants include a significant portion of the urban and rural population in many countries. It manifests itself most significantly in those agglomerations whose centers are large cities. In the last 10-20 years, the importance of such territorial population movements has increased significantly.
The spread of commuter migration has been facilitated by the development of transport networks that provide regular communication between nearby settlements.
Type: seasonal
Seasonal migration is the movement of the working-age population to places of temporary work, mainly for several months, while maintaining the possibility of returning to places of permanent residence. They arise because the economy of some areas consists largely of industries in which the need for labor is uneven over time. During the seasons of the greatest volume of work, the production of these territories requires a larger number of workers, which exceeds the usual requirement, and since this cannot be satisfied by local labor resources. Industries with a seasonal nature of production include primarily agriculture, as well as logging (rafting), fishing (coastal fishing) and a number of others.
Type: permanent
It is also called irrevocable, complete, that is, it is completed forever. Permanent migration simultaneously meets two conditions:
- the population moves from one settlement to another;
- movements are accompanied by a change of permanent residence.
As a result of such displacement, changes occur in the social and ethnic composition of the population in regions and countries. Constant migration is also associated with the transformation of the linguistic environment, during which new languages are learned and language differences are leveled out. In addition, against this background, ethnolinguistic and ethnosocial conflicts also arise.

Migration processes. Problems of the region.
| What reasons can cause the population of a given territory to change? What is the reason for the decrease in the population of our region since 1990? |
Mechanical movement (migration) of the population.
The main reason for population movement is the desire of people to live better. The exception is forced relocations (major disasters, wars, deportations, division of the state).
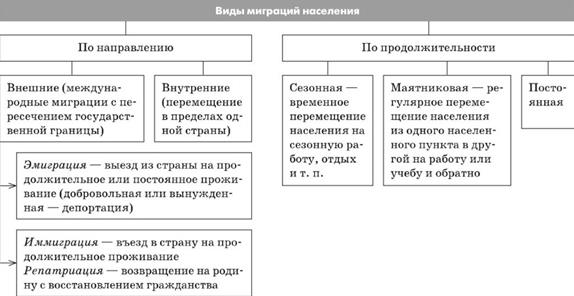
Migrations are classified according to various criteria. Thus, according to the direction of migration flows, they are divided into external (interstate) and internal (within the territory of one country).
External migrations are divided into emigration (moving outside the state) and immigration (entering the country). Based on duration, migrations are distinguished between permanent and temporary.
Permanent (irrevocable) migration is a movement of population that is accompanied by a change of permanent place of residence. An example of permanent migration is the relocation of rural residents to cities, and temporary (reverse) migration is a trip with return (to study, work in another locality, region, state). In this case, temporary migrations are divided into pendulum, cyclical, and episodic.
|
Rice. 1. Types of population migrations
Commutative migration is considered to be daily or weekly trips of the population from places of residence to places of work or study. A significant part of the urban and rural population participates in pendulum migrations. The radius of pendulum migration for large cities can be 40–70 km, and for medium-sized ones – 25–30 km.
Cyclic (seasonal) migration is the movement of the working-age population for a certain time, mainly for seasonal work. Episodic migration includes business, health and other trips that are carried out irregularly.
The driving motives for migration are divided, first of all, into economic ones, related to the search for places with a higher standard of living; and political, caused by changes in state borders and discrimination against certain groups of the population.
Migration processes are characterized by a number of quantitative indicators. The most common of these is the migration balance. Migration balance is the difference between the number of people who arrived in a certain territory and the number who left over the same period of time. This term is synonymous with mechanical population growth. Balance
migration can be positive and negative. This indicator can be expressed in both absolute and relative terms.
Rice. 2. Reasons for migration
In January–October 2014, taking into account all migration flows, 25,402 people arrived for permanent residence in the Donetsk region. The number of people leaving (including migration within the region) amounted to 33,766 people. Migration reduction for January–October 2014
amounted to 8,364 people.
Almost 56% of all those leaving the region are due to family circumstances. Due to a change in their place of work, 4.7% migrated, every fifth went to study. In addition, every tenth migrant is a child leaving with his parents. The migration decline in the region's population continues to negatively affect its age structure and labor potential. It should be noted that the migration activity of the population of different ages is not the same. The most mobile are young people aged 18 to 34, seeking to get a job, education or start a family.
The region is characterized by mechanical population decline and intraregional migration. Basically, the population movement occurs from small towns and workers' settlements to large cities (up to 40% of migrants). There is still a movement from rural areas to cities, mainly large ones (about 30%). Approximately half of this number (15% of all migrants) are those moving from depressed cities (mainly small and medium-sized mining towns). Another 10% move from one area to another (Lugansk region). Less than 5% of migrants leave large cities in search of housing in small towns, and older people are also returning to rural areas. Large cities attract mainly young people due to the opportunities they offer in business, education, employment, and better social conditions.

Summarizing the analysis of migration processes in our region, we can conclude that the reasons for migration are the unstable state of the economy, especially in small towns and settlements.
Problem! One of the acute problems of migration of the region's population is that, having left for other countries, mostly young and middle-aged people generally do not intend to return. For our region, this is not only a loss of working-age population, but also a negative impact on natural population growth with a further deepening of the demographic crisis. What do you think should be done in the region to bring emigrants home?
Problems of the region.
A decrease in the birth rate, a high mortality rate compared to the birth rate, a significant scale of premature mortality, especially among men, an increase in the migration outflow of the population - all these phenomena negatively affect the demographic situation and lead to a further reduction in the population of the region. The problem of survival in the modern period is associated, first of all, with two negative demographic processes - aging and depopulation of the population.
The aging of a people is the increase in the significant weight of older generations in it, compared to the middle and younger ages. If the proportion of people over 60 years of age exceeds 10%, then the nation belongs to an aging nation. In the Donetsk region, the population of this group is more than 20%.
Depopulation and the aging of the nation should be combated with the help of demographic policy - a set of measures aimed at regulating the population. In the Donetsk region, demographic policy should be aimed at increasing the birth rate and reducing mortality. It must be carried out through economic, social, propaganda and other measures. A number of reasons are also significant, including: a difficult economic situation, a high concentration of heavy industrial enterprises with large-scale waste and harmful emissions, a difficult environmental situation, as well as high population density, and, consequently, an increased need for housing and other facilities social infrastructure. The social sphere of our region was financed on a residual basis, which affected its material and technical base, working conditions and quality of life of the population. A particularly difficult demographic situation is developing in mining towns and villages, where there is a need to restructure production.
Thus, despite the increase in the birth rate, the demographic situation in the Donetsk region is still regarded as a crisis. Consequently, the problem of improving the demographic situation for this region is relevant. The solution can be found, first of all, in general
improving the region's economy, adopting social and economic programs.
Table 1. Distribution of migrants by flow and type of settlement in
January-April (donetskstat.gov.ua) (person)
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||
| Number of arrivals | Number of dropouts | Migration increase, reduced (–) | Number of arrivals | Number of retirees | Migration increase, reduced (–) | |
| Urban settlements and rural areas | ||||||
| Total | 12 153 | 12 051 | 12 395 | 12 490 | –95 | |
| Including: | ||||||
| Intraregional migration | 7 906 | 7 906 | X | 8 672 | 8 672 | x |
| Interregional migration | 2 642 | 3 699 | –1057 | 2 634 | 3 373 | –739 |
| Interstate migration | 1 605 | 1 159 | 1 089 | |||
| Urban settlements | ||||||
| Total | 10 700 | 10 337 | 10 663 | 10 552 | ||
| Including | ||||||
| Intraregional migration | 6 705 | 6 484 | 7 235 | 7 028 | ||
| Interregional migration | 2 425 | 3 426 | –1001 | 2 375 | 3 099 | –724 |
| Interstate migration | 1 570 | 1 143 | 1 053 | |||
| Countryside | ||||||
| Total | 1 453 | 1 714 | –261 | 1 732 | 1 938 | –206 |
| Including | ||||||
| Intraregional migration | 1 201 | 1 422 | –221 | 1 437 | 1 644 | –207 |
| Interregional migration | –56 | –15 | ||||
| Interstate migration |
Table 2. Migration movement of the population for January-November 2014
(donetskstat.gov.ua) (person)
| Number of arrivals | Number of dropouts | Migration increase (decrease) |
| Our region | — 9581 | |
| Donetsk (city council) | — 6637 | |
| Avdeevka | — 90 | |
| Artemovsk (city council) | ||
| Ugledar | — 13 | |
| Gorlovka (city council) | — 831 | |
| Debaltsevo (city council) | — 81 | |
| Dzerzhinsk (city council) |
| Dimitrov (city council) | |
| Dobropolye (city council) | |
| Dokuchaevsk (city council) | — 29 |
| Druzhkovka (city council) | |
| Yenakievo (city council) | — 437 |
| Zhdanovka (city council) | |
| Kirovskoe | — 45 |
| Konstantinovka | — 135 |
| Kramatorsk (city council) | — 354 |
| Krasny Liman (city council) | |
| Krasnoarmeysk (city council) | — 109 |
| Makeevka (city council) | — 552 |
| Mariupol (city council) | — 144 |
| Novogrodivka | |
| Selidovo (city council) | |
| Slavyansk (city council) | — 416 |
| Snezhnoye (city council) | |
| Torez (city council) | — 179 |
| Khartsyzsk (city council) | — 292 |
| Shakhtersk (city council) | — 208 |
| Yasinovataya | — 82 |
| Districts | |
| Amvrosievsky | |
| Artemovsky | |
| Velikonovoselkovsky | — 127 |
| Volnovakhsky | |
| Volodarsky | — 40 |
| Dobropolsky | — 5 |
| Konstantinovsky | — 44 |
| Krasnoarmeisky | |
| Krasnolimansky | |
| Maryinsky | |
| Novoazovsky | — 8 |
| Alexandrovsky | — 142 |
| Pervomaisky | |
| Slavic | — 81 |
| Starobeshevsky | |
| Telmanovsky | — 44 |
| Shakhtarsky | — 53 |
| Yasinovatsky | — 34 |
Table 3.
| Overall arrival rate (per 10,000 population) | 69 ,6 |
| Overall attrition rate (per 10,000 population) | 93, 8 |
| Overall rate of migration increase (decrease) (per 10,000 population) | -2 4 , 2 |

| QUESTIONS AND TASKS 1. Consider the “Classification of Migration” scheme. What is emigration and immigration called? 2. Name the reasons for economic, seasonal, political and other migrations. What is the difference between physical migration and intellectual migration? Voluntary versus forced? 3. Determine what types of migration the following cases belong to: - Sixth-grader Andrei was taken to his grandmother in the Lugansk region for the summer holidays. — The entire Levin family is moving to Israel permanently. — Young spouses Yuri and Natalya spent September at one of the resorts in Spain. — Igor’s family lives in Donbass. To support her financially, Igor goes on a shift to Western Siberia to extract oil. He works for three months and spends a month with his family. — Professor Sergeev received an invitation to lecture at the Faculty of Chemistry at the University of Cambridge and at the same time work in the laboratory to create a new drug. |
PRACTICAL TASKS
1. Analyze the data in Table 1. “Distribution of migrants by flow and type of settlement.” Explain changes in migration flows. Compare with data from 2013. Explain the reasons.
2. Analyze the data in Table 2. “Migration movement of the population for January–November 2014.” List the cities with positive migration growth. Explain the reasons.
3. Prepare an educational project: “Problems of the population of our region and ways to solve them”
| FROM THE DIARY OF A LOCAL HISTORY: Population migrations in ancient times had other reasons, forms and directions. The reason for the migration of ancient people was the voluntary or forced development of uninhabited territories. The latter could occur due to climate changes, farming conditions, long-term military conflicts, and population growth. |
Migration of the population was the most important event in the life of mankind and its development. Thanks to migration, we can observe the diversity of races and ethnicities of the Earth's population. People occupied the entire habitable territory. Thanks to migration, millionaire cities, urban agglomerations and clusters of agglomerations (conurbations) were created.
In the modern world there are many states whose creation they owe to migrants. Thus, recently (by historical standards) the USA and Australia, New Zealand and Canada were formed. Today, hundreds of millions of people take part in migration processes.
Table 1. Leading countries in migration flows and
number of refugees.
| Countries of emigration | Countries of immigration | Countries of "refugees" |
| Turkey, Pakistan, India, Philippines, China, Cuba, Egypt, Paraguay, Chile, Ireland, Mexico, Algeria. | USA, Israel, Germany, France, UK, South Africa, Switzerland, Sweden, Saudi Arabia, UAE. | Afghanistan, Rwanda, Iran, Cyprus, Lebanon, Angola, Liberia, Former Yugoslavia, Mozambique, Sudan. |
Types of migration in Russia
In order to understand what types of migration processes prevail in our country, you first need to understand what types of migrants exist on the territory of the Russian Federation.
As you know, in Russia it is customary to call a migrant a foreign citizen who has arrived in the country for a place of temporary or permanent residence or stay.
According to the international classification, the following categories of migrants can be distinguished in the Russian Federation:
- Foreign citizens who arrived in the Russian Federation to obtain an education or undergo vocational training.
- Migrants who have families in Russia or who plan to create one on the territory of the Russian Federation.
- Labor migrants. This category includes foreign citizens working under a contract, carrying out a specific project on the territory of the Russian Federation, temporarily employed foreigners, as well as their close relatives.
- Immigrants who arrived in the country and have the opportunity to freely find work on the territory of the Russian Federation due to family connections, ethnic origin, as well as migrants of retirement age.
- Forced refugees, foreigners and persons without citizenship who are allowed to stay in the Russian Federation for humanitarian reasons, foreign citizens and stateless persons to whom Russia has granted temporary asylum or assigned temporary protection status.
Educational migration occupies an important place in Russia. It is worth noting that Russian educational institutions are especially popular among residents of the CIS and nearby foreign countries, while some Russians prefer foreign universities.
Labor migrants
Every year more and more foreigners come to Russia to find work. Today, labor migrants in Russia, as a special social group, make up the largest number of visitors. This is due to the lower standard of living of the states neighboring the Russian Federation, whose residents want to improve their financial situation. Many of the visitors subsequently move to our country for permanent residence and take Russian citizenship.
Interregional labor migration in Russia in 2021 shows that the more economically developed regions of the country continue to attract population.
The central regions of the country are especially popular among migrants, as evidenced by the fact that most of the participants in the resettlement program, after the period of compulsory residence in the chosen region, move closer to the capital.
In connection with the accession of some countries to the EAEU, international labor migration in Russia has increased in 2021, as the process of employing citizens from these countries has become much easier.
Read more about how the labor activity of foreign citizens is regulated in Russia.
Migrants represented by refugees and internally displaced persons
Over the past decade, there has been an increase in refugees and migrants in Russia. This is due to the turbulent situation in some neighboring states, whose residents are seeking refuge in Russia. Forced migrants are supported by the state and often remain in the country on a permanent basis.
Forced migrants also have some benefits, but legalization in the new region of the country is much simplified for them, since they already have Russian citizenship.
Read more about the forced migrant status.
Illegal migrants
Unfortunately, many well-developed countries are faced with illegal migration. This is due to favorable social, political and economic conditions in the country where those wishing to move are eager to move.
It must be said right away that illegal migration is a crime associated with violation of the rules of entry into the country, as well as the conditions of stay and residence on its territory; For violators of the migration order, fairly severe punishment is provided, usually ending in deportation.
Labor migrants especially often move abroad illegally.
It is worth noting that stricter new rules for migrants in 2017 may increase the number of illegal migrants, because the forbidden fruit is even sweeter.
Discussion and criticism
With these people, the Concept places emphasis on their adaptation to living in Russian society, as well as on the adoption by the state of measures to prevent the emergence of risks associated with interethnic conflicts, imbalances in the labor market, criminal and other negative manifestations.
Voluntary resettlement program in the Russian Federation
- Increase the share of enterprises with technological innovations.
- Raise Russia in terms of high-tech services and goods on the world market, increase the share of exports.
- Increase R&D costs.
- Expand the share of innovative products in the total volume of industrial production.
- At least five Russian universities should be among the world's leading universities (there are 200 in total).
- Increase the share of funds for scientific research by 30%, increase the number of patents.
- Expand international cooperation and the degree of Russia’s integration into world processes.
- To form a sector of development and research in higher educational institutions, to increase their effectiveness and efficiency.
In the Russian Federation, according to the Law “On Migration Registration of Foreign Citizens and Stateless Persons in the Russian Federation” dated July 18, 2006 No. 109-FZ, state authorities and local governments:
Migration processes in Russia are subject to both negative and positive development factors. Negative factors include the collapse of the former USSR, manifestations of nationalism, terrorism, insecurity of certain sections of the state border of the Russian Federation, deterioration in the quality of life of people and the state of the environment, economic instability and social conflicts. Despite the large number of negative factors, there are also positive ones, for example, such as the development of market relations, the development of labor activity in remote areas of the state.
General concept of migration
Regulation of migration processes is an integral part of the legislation of the Russian Federation. To ensure the regulation of migration processes in labor migration, a number of actions have been created, which the government has directed to regulate this type of migration:
In January 2021, a rule was established stating that foreigners living in Russia do not have the right to use an ordinary passport. This by-law eliminates the possibility of exceptional cases for all states. Only a foreign document is considered a quoted identification document for foreign migrants living in the Russian Federation.
In the economic, political and social life of Russia there is a trend called labor migration of the population. In order to understand this in detail, it is advisable to consider a certain amount of information relating to this issue.
What is labor migration in Russia
In addition, the number of crimes committed by foreigners in the country has increased. It is worth noting that their character is no different from the crimes committed by the indigenous inhabitants of Russia. According to statistics, this is fraud and theft.
Labor migration is divided into internal and external. Internal is associated with the movement of labor resources within the country. The external one is international in nature. Both types of migration, in turn, can be:
Migration situation in Russia
It's no secret that Russia receives a huge number of migrants every year. Mostly foreign citizens come to get a job. It is logical to assume that migration from Central Asia to Russia is the most developed. This can be explained by the fact that countries located in this particular part of the continent, close to the Russian Federation, are economically less developed.
Also, the fact that migrants from CIS countries predominate in the Russian Federation is also influenced by the voluntary resettlement program for compatriots. This is why citizens of neighboring states, whose governments do not provide a decent standard of living, flock to Russia.
It is worth noting that in some countries - former republics of the USSR, Russian education is still highly valued, which provides another migration direction - getting an education in the Russian Federation.
Attracting a flow of migrants to the country, of course, ensures population growth, but the current migration situation in the Russian Federation in 2017, or rather, statistical data suggests that a large number of Russians themselves leave the country every year, they give preference to such industrialized countries as the USA, Australia , Canada, Finland and Germany.
It is no secret that attracting foreign labor contributes to the socio-economic development of Russia. If we take a closer look at how migration and labor markets are connected in modern Russia, we will notice that labor migrants agree to work in enterprises that are less advanced from a technical point of view and for lower wages. Thus, employers have no incentive to modernize industry and increase wages, which significantly affects the standard of living of the population.

There is also an opinion that immigrant workers are used primarily in sectors of the economy, but this is true mostly for labor-intensive sectors. On the one hand, the unpretentiousness and low cost of labor of visitors ultimately increases the competitiveness of the products produced by the economy. On the other hand, dumping in the labor market reduces the wages of local workers, and a massive influx of migrants can provoke an increase in unemployment in the country.
If we analyze the characteristics and level of population migration in the Russian Federation at the present time, the conclusion naturally arises that the composition of the population in the country is gradually changing. Russia compensates for the loss of its own population with migrants from nearby Asian countries, which contributes to an increase in the number of Muslims. As a consequence, this will lead to interethnic conflicts.
Regarding how the directions of migration of the population of Russia have changed in recent years, statistics indicate that the most popular for relocation are the Central, Southern and Northwestern federal districts of the country. This is mostly due to economic reasons. At the same time, the activity of resettlement to the northeastern regions of the country has decreased, despite the fact that they are included in the list of priority settlements within the framework of the voluntary resettlement program for compatriots, migrants are in no hurry to move there.
Unfortunately, modern international migration in Russia leads to a significant decrease in the number of ethnic Russians, and native Russians in general: along with a decrease in population growth, there has been an increase in the number of people leaving Russia.
As a rule, scientists, unique specialists, business representatives, and athletes leave for another country and are replaced by cheap, low-skilled labor resources, which does not contribute to the development of science and technology, nor to the improvement of the economic situation of the country.
Thus, migration and Russia’s economic security are closely related: the former has a huge impact on the latter. The very concept of economic security implies the presence of labor resources capable of providing quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the economy. And these resources, due to the annual loss of population, are replenished precisely by migrants arriving in the country.
Regulation of migration at the state level
Modern Russia is in the top three countries in terms of the scale of migration. Many states with a high standard of living, which, like the Russian Federation, border on less developed countries, are subject to an influx of not only foreigners who have legally entered the country, but also illegal migrants. That is why migration processes require control and regulation by the government.
An analysis of population migration in Russia in 2015 showed that at that time there was indeed a huge number of foreign citizens in the country - about 11 million, however, according to the Migration Department (FMS), not all of them came to the country for the purpose of employment. There was also an influx of foreigners from highly developed countries such as the USA and Germany.
Today, four areas of state regulation in the field of labor migration can be distinguished:
- Establishment of standards and their strict adherence.
- Control of labor recruitment by private entrepreneurs.
- Settlement of disputes and disagreements.
- Development of the social security sector.
The Russian Federation is currently experiencing a major demographic crisis and is unable to limit itself to its own workforce. Migration, as a factor in stabilizing the demographic situation in Russia, is the most real and effective way to increase the size of the state.
Statistics of the national distribution of migrants in the Russian Federation
An interesting fact is that the Russian labor market is mostly replenished by citizens of nearby Asian countries. As Rosstat statistics show, labor migration data in the Russian Federation for 2015 are as follows: 598.8 thousand foreigners entered the country, 40% of whom arrived for the purpose of employment, another 39% indicated a different purpose for the visit, but often got a job for a short period of time. period.
In 2015, the majority of migrants were Ukrainians and Kazakhs. Next on the list are Moldova and Turkmenistan.
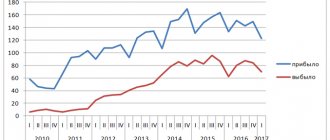
Migration of the population to the Main Administration for Migration of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (FMS) of Russia in 2021 by region in the table shows the influx and outflow of migrants in various regions of the country.
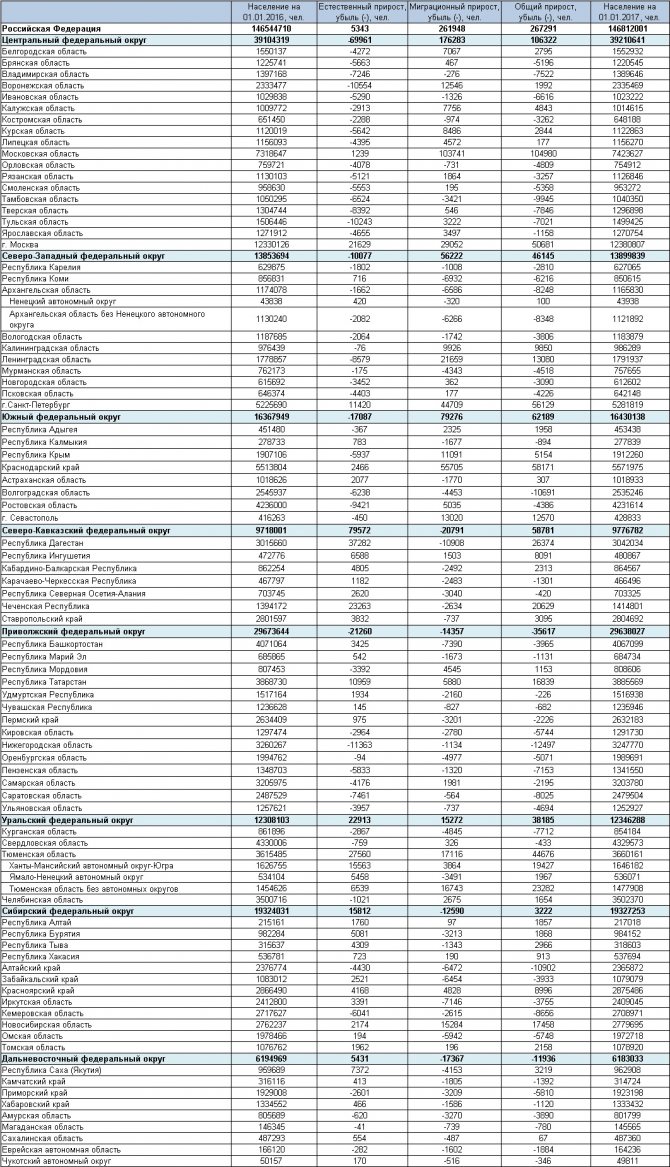
Immigration statistics to Russia in 2021 indicate that foreigners arriving in Russia give preference to the Central, Northwestern, Southern and Ural Federal Districts, since it is in these regions of the country that on average there is an increase in the number of migrants. In other federal districts, despite the fact that in some of their regions there is still an increase in migration, the overall picture shows an outflow of foreign citizens.
How many migrants are there in Russia
Labor migration in Russia is perhaps the most widespread. Today, we can identify several countries whose citizens make up the largest number of labor migrants in Russia in 2021:
- Uzbekistan.
- Ukraine.
- Tajikistan.
- Kazakhstan.
- Armenia.
As for information about how many immigrants there are in Russia in 2017, then, according to data for January-November 2021, which are currently presented on the website of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, their number amounted to almost 14.6 million people, while in the comparable period in 2016 was about 13.27 million people.
Migration indicators in Russia
Statistics for January-December 2021 also include selected indicators of the migration situation in the Russian Federation, which are given below.
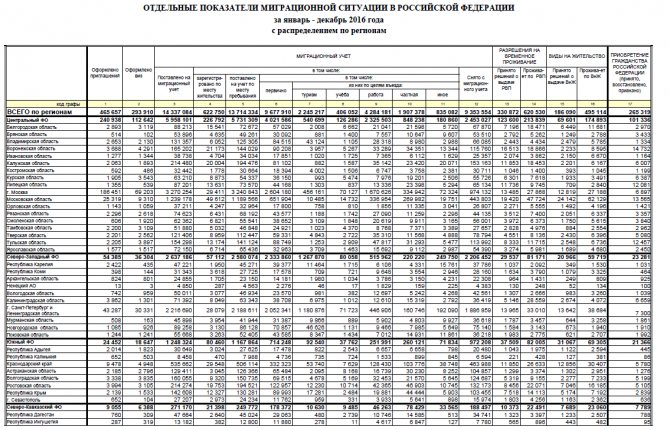
As can be seen from the table, the smallest migration increase in population across Russian regions occurs in the North Caucasus Federal District. There, when entering the country, only 46,263 labor migrants indicated “work” as the purpose of arrival, while the purpose of “private visit” is almost 1.7 times more. A completely different situation is developing, for example, in the Central Federal District, where labor migrants predominate - 2,325,503 people.
In addition, from the table you can find out that in all regions there is a migration outflow of the population - just over 9.354 million, but in the federal districts as a whole it does not exceed the increase in migrants: almost 14.337 million were registered for migration. Thus, the population is still increasing.
What rights do migrants have?
The Constitution and legislation of the Russian Federation enshrines the personal, economic, social rights and freedoms of migrants; they only do not have political rights, that is, they do not have the right to participate in elections, referendums, etc.
The legislation of the Russian Federation gives visiting foreigners not only responsibilities, but also rights.
For example, the rights of migrants in Russia when checking documents in 2017, as well as Russians, are regulated by paragraph 4 of Article 5 of the Law “On Police” of February 7, 2011 No. 3-FZ: when contacting a citizen of the Russian Federation or another state - it doesn’t matter , the police officer is obliged to state his position, rank, surname, and state the reason and purpose of the appeal.
In this case, foreign citizens and stateless persons must have not only an identity card, but also documents confirming their legal status as migrants in the Russian Federation.
Checking documents by police officers is justified only in some cases; they must have information that gives grounds to suspect a person of committing a criminal or administrative offense or that the person is wanted.
As noted above, on the territory of the Russian Federation, migrants have all the rights and freedoms of Russian citizens, with the exception of political ones. For the most part, the sources and principles of migration law are based on state legislation.
Read more about what assistance can be provided to migrants.
What problems do migrants face in the Russian Federation?
It must be remembered that labor migration has not only positive aspects, but also negative ones, both for the receiving party and for the country providing the flow of labor.
The problems of Russia's participation in labor migration are compensated by legislative acts aimed at regulating the migration influx and ensuring economic security. It is also worth noting that migration policy is strongly influenced by national interests.
If we consider the problems of migrants in Russia, then the main, primary problem is legalization in the country. Not all foreigners who enter the country for the purpose of employment have a contract in hand or enter into an employment contract in the first week. The search for a job sometimes drags on and you have to look for a reason to extend your stay in the country. It is also worth noting that migrants may not apply for all vacant positions, since there are some restrictions on the choice of professions for them. Another difficulty is the availability of permits that an applicant for a particular vacancy must have.
It's no secret that many visiting foreigners accept low-paying jobs. On the one hand, migrants fill vacancies that not all Russians will agree to, and on the other hand, a migration problem arises, since labor in the country begins to depreciate against this background, while the standard of living should, on the contrary, increase.
Crime by migrants
Another negative consequence of migration is administrative and criminal offenses. The criminological characteristics of crimes committed by migrants in 2021 are not yet presented on the website of the Ministry of Internal Affairs; there is data only for January-September: 31,600 crimes committed by foreign citizens were registered, 12,000 committed against them.
If you look at the available statistics of the department, for example, for the period 2010-2015, you can note that the number of crimes committed by foreign citizens and stateless persons on the territory of the Russian Federation varies - from 49,000 to 44,400.
It is worth noting that crimes among migrants in Russia are committed not only by foreigners who are in the country illegally, but also by those who are in it legally. Most often, these are robberies and drug trafficking. The number of crimes against migrants themselves also ranges from 11,400 to 16,000.
Prevention of migration crime is one of the most important areas of migration policy of the Russian Federation. The state, first of all, is improving mechanisms for controlling the movement of illegal migrants and systems for registering the arrival/departure of foreign citizens. Databases of labor migrants are being created. Territorial bodies of the Main Directorate for Migration Affairs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs carry out comprehensive measures to check the documents of migrants in order to identify illegally residing citizens. Information resources are constantly monitored to search for advertisements that offer illegal acquisition of Russian citizenship, temporary registration, and the issuance of migration cards and passports.
Changes to immigration legislation in 2021, which involve tightening some rules and deadlines, will also help reduce crime.

Amnesty for migrants
In the spring of 2021, a migration amnesty was launched, which allowed migrants from Tajikistan who were illegally in Russia or who had committed minor offenses on its territory to legalize their legal status.
Who will be covered by the amnesty?
This program is provided only for citizens of Tajikistan, and migrants who have been denied entry to Russia due to repeated violations over three years with subsequent administrative liability can fall under its action. Also, the amnesty can be used by Tajiks who violated the period of stay in the country and did not leave it after 30 days from the date of entry.
Find out details about who is blacklisted as migrants and why.
How do Russian citizens feel about migrants?
The number of migrants in Russia is very large, which creates no less problems, and in this regard, migration issues have to be resolved.
On the one hand, we can say that due to migrants, the demographic security of the Russian Federation increases, since the population is growing, the birth rate is correspondingly increasing, and jobs are being filled. At the same time, there are fewer ethnic Russians, Russian culture is gradually disappearing, since in most cases visiting foreigners adhere to their own culture and traditions. All this, of course, cannot cause approval from the indigenous inhabitants of the country.
Thus, those who are planning to move to Russia for permanent residence need to be prepared for the fact that not all Russian citizens will be happy with such a decision.
The state, however, shows a loyal attitude towards migrants, an example of which is the social protection of migrants in the Russian Federation. In 2000, Russia signed (not ratified) the 1996 European Social Charter, which provides for the obligation of member states to take measures through appropriate international agreements to ensure equality of citizens of member states in the field of social security, including social services, in the event of migration workers from one country to another. Thus, foreigners temporarily or permanently residing in Russia can use many social services along with Russians, for example, receive medical care, get a job, and migrant children can attend kindergartens, schools, etc.
Grand total
Population migration in its various manifestations has existed from time immemorial, because it is not for nothing that in historical science there is even a conventional name “Great Migration of Peoples” - the period from the 4th to 7th centuries, when peoples from the periphery of the Roman Empire moved to the metropolis. But the reason for the emergence of this process has always been completely different phenomena in society and nature. At the dawn of mankind, these were, in most cases, natural disasters and the desire to find another region with better opportunities for food and development; nowadays, to this it is worth adding political disasters and a person’s desire to realize himself professionally.
Today there are many people who want to move to Russia, and migration processes have not bypassed Russia. Currently, it is difficult to find a Russian who does not know who immigrants are in Russia, since a huge part of the economy is developing with their help. The need for population growth forces the state to take measures to attract foreign citizens. The loss of its own population is compensated by migrants, which ensures economic development and prevents a demographic crisis.
International experts admit that Russian immigration laws are quite advanced. To provide the necessary quantity of labor in the country, to protect the national labor market, to prevent violations of international legislation, international law and the rights of foreigners and stateless persons - these are the main goals pursued by Russia’s migration policy. Migration law should not only regulate all human movements, but also act in the interests of the state and its citizens.