Economic cycles and changes affect individual countries differently, but leaders tend to maintain their positions in all conditions. The world's strongest economies have not changed dramatically since 1980. Only 3 new states appeared in the top twenty.
Moreover, key players hold the majority of the world's wealth. The top ten economies account for 68% of the world's nominal GDP, while the top twenty account for 81%. The remaining 172 countries produce less than 1/5 of global economic output.
To compile this rating, we analyzed the statistics of the IMF (International Monetary Fund) and talked about the economy of each country separately.
USA
- Nominal GDP: $21.44 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $21.44 trillion

Source: ru.wikipedia.org
The United States has maintained its status as the world's leading economy since 1871. In 2019, in nominal terms, its volume amounted to $21.44 trillion. In 2020, $22.32 trillion is predicted.
This country is often called an economic superpower because it makes up almost ¼ of the world economy and is distinguished by the development of infrastructure, technology, and an abundance of natural resources. And this despite the fact that 80% of the country's gross domestic product comes from the service sector.
When assessed on the basis of purchasing power parity, the United States loses first place to the People's Republic of China and lags behind by $6 billion. According to Navy forecasts, the gap will widen, and by 2024 the United States will have $25.79 trillion, and the PRC will have $39.81 trillion.
Differences
Developed economies are those with a high gross domestic product (GDP) per person, a decent standard of living, and an equal distribution of benefits among all citizens. In these countries, services in the economy (education, health care, food, recreation, etc.) predominate over agriculture and industry, but highly developed industry provides countries with goods and influences economic growth. Such countries have modern and high-quality infrastructure.
These countries have economic systems that support stable economic growth and prosperity.
Developing countries include those states that have low gross product and income per person, and have some economic dependence on other countries (in terms of the financial system, trade and the need to export resources). There is no strict definition, but developing countries can be called those states that are not members of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, because these countries do not have the characteristics of member countries of this union, namely:
- Compliance with democratic principles.
- Free market economy.
- High degree of industrialization.
- Guarantees of human rights.
- Social programs to support the population.
Many of the developing countries have high production rates and fast-growing economies (China, Russia, Qatar) and have an average level of economic system development and average levels of prosperity.
Those countries that are characterized by a predominant level of development over other countries with a developing economic system, but which do not yet have all the characteristics of developed countries, are called “newly industrialized countries”.
Among the economically weak countries, it is worth noting those with the lowest level of economic development and low rates of increase in national welfare, the absence of large-scale production and a large proportion of the population below the poverty line.
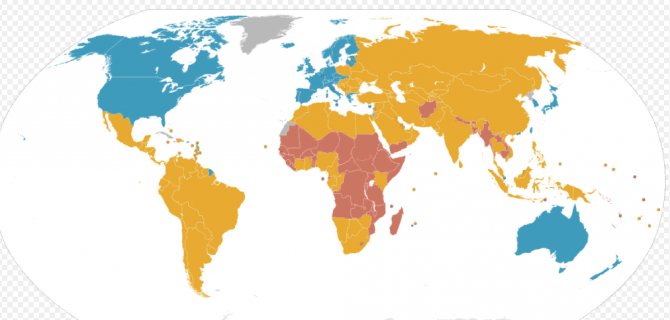
Map of developed and developing countries: developed economies (blue), rapidly developing economies (yellow), less developing economies (red)
As can be seen from the map, developed countries include almost all European countries, some Asian and Arab countries, as well as the United Arab Emirates, the USA and Canada. Countries with low living standards and weak economies are mainly located in Africa. Approximately half of the world's GDP comes from countries marked in yellow and red.
China

- Nominal GDP: $14.14 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $27.31 trillion
The strongest economies in the world cannot do without the Celestial Empire. Over the past few decades, China has achieved exponential growth by overcoming the barriers of centralized closed trade. It is now a manufacturing and export center, sometimes called the "factory of the world."
In 1980, China was in the TOP 20 in seventh place with $305.35 billion in GDP. The US then had $2.86 trillion. Thanks to reforms begun in 1978, China actually began to increase its GDP by 10% every year. Recently, these rates have slowed, although they remain very high.
The World Bank, speaking about the surge in China's economic growth in 2017, refers to the cyclical recovery in global trade. The organization predicted growth of 6.6% in 2021, and it was right. In 2021, growth was 6.1%. Gradually, by 2023, according to experts, it will decrease to 5.6%.
Due to its large population, China is not among the leaders in terms of GDP per capita - $19,500 (74th place in the world).
The richest countries by GDP per capita
The UN, in order to take into account all economic factors, prefers to consider countries where the GDP per capita is higher to be the richest. It turns out that residents have more access to the country's wealth and therefore live in greater prosperity.
If you recalculate the ranking using this modifier, it turns out that completely different countries are the richest.
Qatar ($126 thousand per capita per year)
The richest country in the world is actually Qatar, a small state in the east of the Arabian Peninsula. Moreover, just some 50-60 years ago it was an extremely backward country with an agricultural economy. However, discovered oil and gas reserves helped Qatar achieve breakthrough successes over several decades.
Profits from the sale of oil, gas and derivative products account for about 70% of the country's budget. The steel industry, construction, and fertilizer production are also actively developing.
In order to maintain its status as the richest country in the world in the future and not depend on energy prices and their reserves in general, Qatar is developing information technology, the service sector and tourism.

Luxembourg ($104 thousand)
The small state of the Duchy of Luxembourg is located in the very center of Europe. It is, without exaggeration, the economic heart of the Old World. Luxembourg is an offshore zone, so thousands of headquarters of international corporations have found residence there. Tourism, trade, and financial services are very developed here.
In addition, Luxembourg is the largest supplier of iron, steel and iron - a significant part of its GDP is made up of ferrous metal exports.

Singapore ($90 thousand)
Singapore is a city-state. Until recently, it was just another depressed region of Asia, experiencing enormous economic difficulties. And now it is a large industrial center producing electronics, software, and medicines.
There are no mineral resources in Singapore, and the budget is replenished by income from high-tech manufacturing, biotechnology and air travel - the city owns its own airline, Singapore Airlines, one of the largest on the Asian continent.
Like Luxembourg, Singapore is an offshore zone. Thanks to a competent policy of attracting foreign investment, the country was able to become the richest in Asia.

Brunei ($76.8 thousand)
Another South Asian “tiger” of the new generation. Brunei's wealth comes from its large oil and gas reserves. The country's economy is entirely raw materials - sales of petroleum products bring about 90% of total income.
However, the sultanate has done little to diversify the economy. On the contrary, large investments are being made in the oil production sector. Thus, a new ethanol production plant was recently launched.
What Brunei will do when energy reserves run out or prices plummet is still unknown.

Ireland ($69.9 thousand)
Ireland entered the TOP 10 richest countries in the world in 2015 - and quite unexpectedly. After the banking crisis, the government took a number of unprecedented economic measures, completely changing the tax system - and indeed the way of life of the population in general. As a result, in 2015 Ireland's GDP grew by 30% - this is an absolute record among developed countries.
Now GDP growth has dropped to “only” 5% per year. Ireland has a very diversified economy. The main income comes from exports - the country sells fish, grain, electronics, medicines, software, textiles, cars and equipment, etc. to other countries.

Norway ($69.2 thousand)
The kingdom's main income is revenue from the sale of oil and gas (almost 30% of the budget). In addition, huge amounts of iron, titanium, aluminum and wood are mined in Norway. The kingdom is also a recognized leader in fish exports.
What’s interesting is that Norway’s energy needs are almost completely covered by the use of renewable sources: water and wind. As a result, all oil produced is exported.
The proceeds are invested in the development of the services and information technology sectors, as well as in shipbuilding. Stable incomes allow us to keep inflation at a record low level - only 3% per year.

Kuwait ($69.1 thousand)
The Sheikhdom of Kuwait is considered one of the most urbanized countries in the world. 95% of the budget and 50% of GDP are revenues from the sale of petroleum products. Kuwait owns about 9% of all world oil reserves.
At one time, Kuwait suffered greatly due to the Gulf War, but now it has been able to regain its position. Every year the country gets richer. The government is actively investing, pouring money into the service sector and construction.
Local residents have the right to free medicine and education, and upon the birth of children a large benefit of several thousand dollars is paid. However, emigrants (of whom there are almost 55% in Kuwait) do not have any benefits or special rights.

United Arab Emirates ($67.8 thousand)
Another oil country from the Arabian Peninsula. The main income here comes, as you might guess, from the export of “black gold”. Most of the oil is produced in the emirate of Abu Dhabi.
The UAE is actively developing tourism and foreign trade, as well as construction and re-export. Hotels in the Emirates are considered the most expensive and prestigious holiday destinations in the world, and in shopping centers you can easily find absolutely any world brands.
An interesting fact is that every tenth resident of the UAE is a millionaire.

Switzerland ($59.5 thousand)
The Swiss Confederation is considered one of the most prosperous and stable economies in the world. The country is famous not only for watches, cheese and Alpine chocolate, but also for its special banking system. Swiss banks are the most reliable in the world, and banking secrecy is protected at the state level. Monetary policy is such that it is quite profitable to keep large sums of money in local banks.
Switzerland is an offshore zone, so quite a lot of different high-tech companies are registered there. The country is also known for its loyal attitude towards cryptocurrencies – this is where Litecoin and Etherium appeared.
Interestingly, almost 70% of Switzerland’s budget comes from tourism – mainly ski and medical tourism.

Hong Kong ($41.3 thousand)
Another city-state in our TOP of the richest countries in the world. Hong Kong is rightly called the financial brain of Asia. This is the center of Asian remittances and the main offshore zone for Chinese corporations.
Pharmacology, tourism, cooking, as well as high-tech manufacturing and the IT industry are actively developed in the country. The chemical and biochemical fields of activity have great potential.
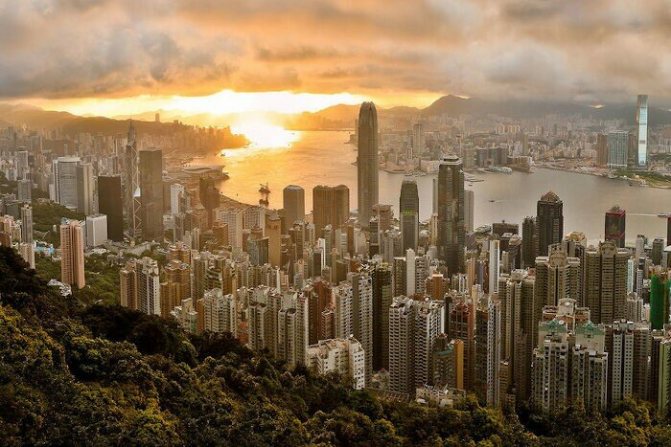

Hong Kong actively attracts foreign investment in the construction sector - the city's area is small compared to the number of residents. The density in the region is 6,400 people per 1 square kilometer, so the government is looking for new solutions in architecture.
Interestingly, Russia in terms of GDP per capita ranks only 62nd in the world with 10.6 thousand dollars. This is only slightly higher than the global average of $10,000. According to this indicator, we are exactly between Turkey and Romania, with countries such as Panama, Chile, Equatorial Guinea and Lebanon ahead of us.
Japan

- Nominal GDP: $5.15 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $5.75 trillion
The 2008 financial crisis rocked the Land of the Rising Sun as it was accompanied by weak domestic demand and huge public debt. In addition, after the peak came out, a strong earthquake occurred, which hit the economy and social sphere. But by 2021, Japan's economy has surpassed the nominal GDP mark of $5 trillion. Forecast for 2021 – $5.59 trillion.
The Japanese economy will receive an additional stimulus for the 2020 Olympics, which always attracts investment to the host country. The strengthening is also facilitated by the Bank of Japan's tight monetary policy.
In 2021, GDP per capita was $45,550, the thirty-first figure in the world.
Rating of countries in the world by level of social progress
The Social Progress Index is a composite indicator of the international research project The Social Progress Imperative, which measures the achievements of countries around the world in terms of social well-being and social progress. Developed in 2013 under the leadership of Michael E. Porter, Chairman of The Social Progress Imperative, a Harvard University professor and expert in strategic management and international competitiveness. The Index's editorial board includes representatives from a number of leading universities and research centers, including Harvard Business School and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.The authors of the study believe that the concept of social progress has become one of the most important areas of research in the field of sociology, psychology, economics and public administration, therefore indicators of social development are often considered as a certain alternative to indicators of economic development, which is a necessary but insufficient condition for social progress. The index does not include indicators of economic development of countries around the world (such as the level of GDP and GNI), but is intended to assess social well-being in a particular country. Because the study measures social achievements separately from economic indicators, it allows for a deeper examination of the relationship between economic and social development.
The index covers countries for which reliable indicators are available and is based on a combination of data from public opinion polls (12%), assessments of development experts (25%) and statistical information from international organizations (61%). The report's cross-country analysis of social development factors informs comparisons and provides detailed profiles of each country, including details of their overall ranking and guidance on their key strengths and weaknesses.
When determining the success of a country in the field of social progress, over 50 indicators are taken into account, combined into three main groups:
- Basic human needs are food, access to basic medical care, housing, access to water, electricity and sanitation, and the level of personal safety.
- The foundations of human well-being are access to basic knowledge and the level of literacy of the population, access to information and means of communication, the level of healthcare, environmental sustainability.
- Opportunities for human development - the level of personal and civil freedoms, ensuring the rights and opportunities of a person to make decisions and realize their potential.
The index measures each country's achievements on a scale from 0 (least resilient) to 100 (most resilient) based on data collected in the three core categories above. A detailed description of the methodology for forming the Index and data sources for it is provided in the annual release of the ranking based on the results of the next comparative study.
Germany

- Nominal GDP: $3.86 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $4.44 trillion
Germany has not only the largest but also the strongest economy in Europe. It is fourth in the world when assessed by nominal GDP. GDP at purchasing power parity is $4.44 trillion, and per capita is $53,570 (20th place). In 1980, the German economic volume was $850 billion, which was enough for third place in the ranking.
Germany was heavily dependent on the export of capital goods, and this increased the impact of the 2008 crisis. The economy grew 2.2% and 2.5% in 2021 and 2021. In 2021 and 2021 – by 1.5% and 0.5%. Forecast for 2020 – 1.2%.
The launch of Industry 4.0 contributes to Germany's continued economic strength. This is a strategic initiative to create a leading market and provider of advanced manufacturing solutions to the world.
The richest countries in the world by absolute GDP
Among economists, a country's GDP is considered a universal indicator. It reflects how many products are produced in the country, as well as services provided. GDP depends on many indicators, mainly the level of production, price growth, employed working population, etc.
Countries are assessed by GDP level by the IMF, the UN, and the World Bank. Each organization offers its own methodology for calculating this indicator. However, in the end the summary graph looks about the same.
1st place - USA
The most powerful economy, according to the IMF, is still that of the United States of America - this country accounts for about 20% of world production. The US GDP in 2021 is about $21.5 trillion, making the US the richest country in the world . According to World Bank forecasts, the country's economic growth will be 2.5% in 2021 and 1.7% in 2021. The main growth drivers are:
- large reserves of natural resources;
- developed infrastructure;
- advanced science;
- powerful political influence of the country.
Despite the confident position of the United States, other countries with rapidly developing economies are nipping at the heels of this country.

2nd place - China
In second place in the ranking of the top richest countries in the world is China, and by a large margin. The nominal value of China's GDP is $14.2 trillion. The main growth is provided by the development of high-tech production, as well as the service sector. At the same time, China's GDP growth rate is higher than the United States - about 5-7% per year. At this rate, China will overtake America in terms of nominal GDP by the end of the 2020s.

3rd place - Japan
Japan occupies third place by an even greater margin. Its GDP is $5.2 trillion. The economic development of the Land of the Rising Sun is hampered by deflation, which the government is desperately fighting, as well as the rapid pace of aging of the nation. Many young people, faced with the impossibility of career advancement, move to nearby Asian countries with great growth potential.

4th place – Germany
Germany, with a GDP of $4.2 trillion, ranks 4th in the TOP of richest countries. It is the strongest economy in the Eurozone. Despite all the crises that have rocked the European Union in recent years, as well as its strong dependence on exports, Germany is developing successfully and is not going to give up its position.

5th place - Great Britain
The UK is in 5th place with a GDP of $2.9 trillion. Since 2009, the country's economy has been growing at approximately 2.7% per year. Experts note that the growth rate has slowed recently, and in 2021 an “increase” of only 1.5% is expected.
This is not surprising - the consequences of Brexit have somewhat shaken Britain's position in the world market. Despite some uncertainty in the future, the country's economy continues to develop, and investors are willing to invest in the UK.

6th place – India
The Indian economy grew rapidly from 2003 to 2007 - by about 9% per year. After the 2008 crisis, growth slowed, but the positive dynamics remained. India has managed to overcome the economic slowdown due to the low rupee and lack of a strong technology base.
Now growth rates are returning to pre-crisis levels. Nominal GDP is $2.94 trillion, but already in 2021 India can catch up and overtake the UK in terms of this value. By the end of the 2030s, India's economy could become even larger than China's, according to some estimates. And now it is still 6th in the top richest countries.

7th place – France
In 7th place in the TOP of the richest countries in the world is France with a GDP slightly less than that of India - $2.93 trillion. The economy is expected to grow by 1.6-1.7% in 2019-2020. That is, sunny France will no longer catch up with India in terms of GDP.
But in any case, the homeland of the Eiffel Tower today produces approximately 1/5 of the total gross product of the Eurozone. At the same time, the French economy is largely closed on itself, which makes it possible to endure crisis years relatively safely. Moreover, almost 70% of GDP is services.
The main risk for the French economy is rising unemployment, which the government cannot cope with.

8th place – Italy
Despite the fact that Italy's GDP in 2021 amounted to about $2.16 trillion, its growth rate is gradually slowing down. Italy still cannot recover from the shock of 2008, when the economy fell by more than 5.5% due to the crisis.
The lack of clear economic reforms, general stagnation in the labor market, huge and simply oppressive public debt, high tax burden on business - all this does not contribute to GDP growth. If Italy does not solve its problems in the near future, then most likely it will leave the ranking of the richest countries in the world.

9th place – Brazil
Brazil's GDP reached $2 trillion in 2021. Over the past 10 years, the economy has grown by 3-5% per year, which is an excellent indicator. However, development has slowed down for the following reasons:
- constantly growing inflation rate;
- strict lending conditions;
- high tax rates;
- progressive corruption.
In addition, the hosting of the World Cup in 2014, despite all the prestige, significantly crippled the economy and caused a new surge of discontent in the country.

10th place – Canada
Canada's GDP in 2021 was $1.8 trillion. Like Russia, Canada's economy is a commodity-based economy and largely depends on oil prices. Since 1999, the country's GDP has been growing steadily. Even in the crisis year of 2008, Canada did not suffer so much - the economic decline was only 2.7%, while, for example, the United States lost more than 5% of GDP, and Russia - about 10%.
This is why Canada traditionally ranks first in rankings as the country with the most sustainable economy. The local government manages to achieve this through the wide diversification of industries and close economic ties with the USA, Russia and Scandinavia.

India

- Nominal GDP: $2.94 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $11.33 trillion
India is the country with the fastest growing economy in the world, although it has been slowing down in recent years. In 2021, she took fifth place in the ranking from Great Britain. However, the GDP per capita of this country is far from its leading position - $8,380.
In 1980, the Indian economy was only $189 billion (13th place). In 2021 the economy grew by 6.8%, in 2021 by 6.1%. For 2021, the Navy forecasts growth of 7%.
Post-colonial India was at first a purely agrarian state, but has seriously increased its production and services in recent decades. Today, services make up 60% of the economy and provide 28% of the workforce.
Industry is the second most important segment and is actively stimulated through government initiatives. The agricultural sector accounts for about 17%, but this is still high compared to Western countries.
India's economic advantages now are low dependence on exports, high demographics and a growing middle class. That is why India is rightfully one of the strongest economies in the world.
Rating of countries with investment programs
You can move to some countries that occupy leading positions in the rankings of living standards using the citizenship by investment program.
The ranking of the TOP 5 countries with a high standard of living and having investment programs is as follows: Malta. It ranks 28th in the Human Development Index. Permanent residence in Malta can be obtained within 3 to 9 months by choosing a convenient investment method:
- In government bonds (minimum amount – 250 thousand euros).
- Purchase of real estate (from 550 thousand euros).
- Real estate rental (from 330 thousand euros).
Maltese citizenship can only be obtained after obtaining residence permit status. An investor can also choose a convenient way to invest funds:
- Non-refundable contribution (from 650 thousand euros to a government fund, from 150,000 euros to government bonds).
- Purchase of real estate (from 1,158,200 euros).
- Property rental (from 888,200 euros).
Austria. Austria, being 5th in the IQL and 8th in the HDI, also offers a residence permit/citizenship for contribution to the economy. Only 450 investors can use the program in 1 year. In order to obtain citizenship of a country, it is necessary to invest at least 8 million euros in its economy. Against the background of these conditions, a residence permit in Austria looks more attractive. To do this, it is enough to confirm the availability of funds in a bank account to live in the country (the status does not imply work or creation of a business):
- For one investor – from 21,000 euros.
- For a married couple – from 31,500 euros.
Cyprus. According to the IQL, Cyprus is in 33rd place. However, his program is considered one of the safest, most popular and attractive in the world. The country allows a foreign investor to obtain a residence permit, and until November 1, 2021, non-residents could also count on receiving citizenship for their contribution to the economy. Permanent residence in Cyprus can be obtained for the purchase of real estate in the amount of 300 thousand euros or for placing a deposit in a bank in the amount of 30 thousand euros.
Greece. According to the IQL, Greece is in 43rd place, and in the HDI – 32nd. The golden visa of this country is very attractive - to obtain the status of a Greek residence permit, you need to invest an amount of 250 thousand euros in real estate.
Montenegro. Montenegro, ranked 48th in the HDI, allows foreigners to take advantage of the economic citizenship program and receive a passport in six months. According to its terms, the candidate must contribute 100 thousand euros in the form of a subsidy to the government fund, as well as invest in the construction of tourist facilities:
- In the north of the country - from 250 thousand euros.
- In the south of the country – from 450 thousand euros.
Great Britain

- Nominal GDP: $2.74 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $3.13 trillion
The United Kingdom ranks sixth in terms of nominal GDP, and ninth in terms of GDP based on PPP. The per capita income is $46,830, which puts the country 30th in the world. In 2021, nominal GDP reached 2.74 trillion; by 2023, $3.02 trillion is expected. From 1992 to 2008, the British economy experienced upward trends in every quarter. However, since April 2008, a decline in production volumes has been recorded for five quarters. The economy shrank 6% during that time and took five years to return to pre-recession levels.
Three quarters of the UK economy's GDP comes from the services sector. The second most important segment is agriculture. Despite employing only 2% of workers, 60% of the UK's food needs are produced domestically.
France

- Nominal GDP: $2.71 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $3.06 trillion
France is the most visited country in the world and has the third largest economy in Europe. It provides a high standard of living with a GDP per capita of $47,220.
Economic growth has slowed in recent years and, under pressure from rising unemployment, the government has had to develop a plan to reboot. In 2014-2016, the World Bank recorded an unemployment rate of 10%. By the end of 2021, this figure dropped to 8.5%.
In addition to tourism, which forms an important part of the economic system, France is one of the leading agricultural producers. It accounts for about a third of EU agricultural land.
The country ranks sixth in the world in terms of agricultural production and is second only to the United States in its exports. The manufacturing industry is dominated by the chemical industry, automobile manufacturing and weapons. All this helps France to be among the strongest economies in the world.
Level of economic development
When determining the indicator, many factors are taken into account, and not just actual digital data (GNP, GDP, capital accumulation, etc.). When compiling a ranking of the world's economies, experts take into account:
- development of productive forces;
- improvement of science and education;
- level of culture;
- quality of life of the population.
Countries are usually divided into developed, developing and underdeveloped. Most experts classify the Russian economy as the second type.
GDP
Gross domestic product is a value characteristic of all goods produced on the territory of the country by enterprises, individual entrepreneurs and individuals. When determining the results of labor of the population for the reporting period, economists summarize all incomes or expenses:
- export (excluding import);
- procurement;
- investments;
- consumption.
Countries are divided by GDP level based on data from the World Bank, IMF or UN. In addition to the absolute indicator, there is also a relative indicator, when the result is divided by the number of residents of the state. Current data is shown in the table.
The USA and China are in the lead in the ranking of absolute GDP by a huge margin. However, in terms of relative indicators, China is significantly inferior even to many developing countries.
Economic Freedom Index
This term is developed based on the theory of Adam Smith. Its supporters believe that state intervention in economic life (production, distribution and consumption) causes certain harm to the economy, except in objectively necessary cases, for example, when it is necessary to overcome a crisis, in an emergency situation or in wartime.
Not all countries with developed economies are in the top in terms of freedom of economic activity. This partly proves the arbitrariness of the index.
Public welfare of countries
This index, developed by English analysts in 2006, takes into account several social indicators. The most prosperous countries in the world are presented in the table.
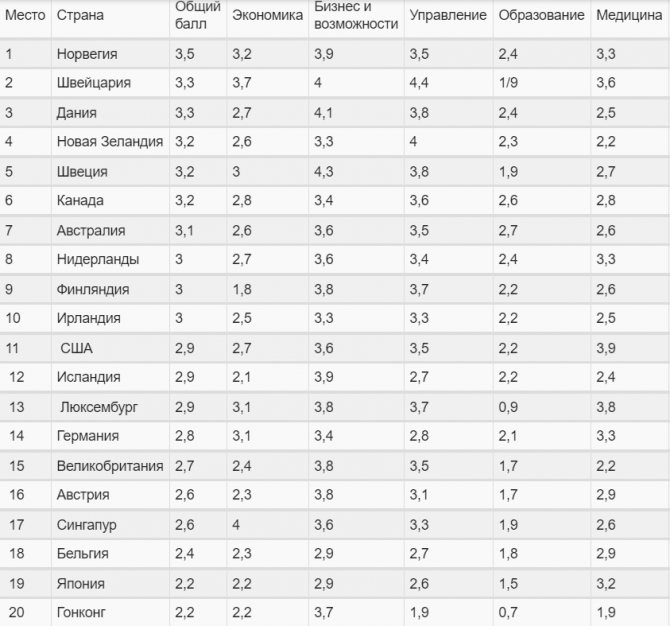
Unfortunately, Russia’s place in this ranking is in the sixth ten. Particularly problematic areas in our country are personal freedom and security, as well as social security.
Other indicators
An important additional index that is usually paid attention to is the HDI. This is an indicator of human development, calculated by a special UN commission since 1990. The following must be taken into account:
- availability of social benefits;
- level of health and life expectancy;
- the degree of accessibility of education and its quality, from preschool level to higher education;
- income ratio;
- mortality analysis.
According to the Human Development Index, countries are divided into 12 groups, and in a simplified format into 4: from very high to low. In this case, Russia is given the highest position. Ukraine remains one step lower – its HDI is simply high.
Sometimes studies are conducted on the topic “The safest country in the world to live in.” It takes into account many threats, including military, terrorist and criminal. Denmark and Iceland have been the leaders for several years.
Italy

- Nominal GDP: $1.99 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $2.44 trillion
Despite its status as a significant member of the European Union, Italy is experiencing problems: unemployment is still about 10% (among young people - 28.6%), political and economic chaos is obvious in the republic. In addition, there is a public debt in the region of 144% of GDP.
But there is a resource for recovery, given stable exports and business investments. Growth of 1.1% and 1.7% was recorded in 2021 and 2021, and 0.9% in 2021. In 2021, GDP remained unchanged. For 2021, the IMF predicts +0.5%.
Brazil

- Nominal GDP: $1.85 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $3.46 trillion
Brazil is the largest country in South America by area and population. Domestic political uncertainty, corruption problems and the end of the so-called commodity supercycle have weakened the country's investment and business environment, but the situation appears to be improving.
In 2006-2010, Brazil gained an average of 4.5%, in 2011-2013 – 2.8%. In 2014, the growth was 0.5%. After a pullback of 3.3% in 2021, a growing trend has emerged again: +1.1% in 2021 and 2018, +0.9% in 2021.
Rating of living standards of the world's population based on the UN report for 2000.
| № | A country | Capital | Part of the world |
| 1 | Norway | Oslo | Europe |
| 2 | Sweden | Stockholm | Europe |
| 3 | Canada | Ottawa | North America |
| 4 | Belgium | Brussels | Europe |
| 5 | Australia | Canberra | Australia and Oceania |
| 6 | USA | Washington | North America |
| 7 | Iceland | Reykjavik | Europe |
| 8 | Netherlands | Amsterdam | Europe |
| 9 | Japan | Tokyo | Asia |
| 10 | Finland | Helsinki | Europe |
| 11 | Switzerland | Berne | Europe |
| 12 | France | Paris | Europe |
| 13 | Great Britain | London | Europe |
| 14 | Denmark | Copenhagen | Europe |
| 15 | Austria | Vein | Europe |
| 16 | Luxembourg | Luxembourg | Europe |
| 17 | Germany | Berlin | Europe |
| 18 | Ireland | Dublin | Europe |
| 19 | New Zealand | Wellington | Australia and Oceania |
| 20 | Italy | Rome | Europe |
| 21 | Spain | Madrid | Europe |
| 22 | Israel | Jerusalem | Asia |
| 24 | Greece | Athens | Europe |
| 25 | Singapore | Singapore | Asia |
| 26 | Cyprus | Nicosia | Asia |
| 27 | Korea South | Seoul | Asia |
| 28 | Portugal | Lisbon | Europe |
| 29 | Slovenia | Ljubljana | Europe |
| 30 | Malta | Valletta | Europe |
| 31 | Barbados | Bridgetown | North America |
| 32 | Brunei | Bandar Seri Begawan | Asia |
| 33 | Czech | Prague | Europe |
| 34 | Argentina | Buenos Aires | South America |
| 35 | Hungary | Budapest | Europe |
| 36 | Slovakia | Bratislava | Europe |
| 37 | Poland | Warsaw | Europe |
| 38 | Chile | Santiago | South America |
| 39 | Bahrain | Manama | Asia |
| 40 | Uruguay | Montevideo | South America |
| 41 | Bahamas | Nassau | North America |
| 42 | Estonia | Tallinn | Europe |
| 43 | Costa Rica | San Jose | North America |
| 44 | Saint Christopher and Nevis | Buster | North America |
| 45 | Kuwait | Kuwait City | Asia |
| 46 | UAE | Abu Dhabi | Asia |
| 47 | Seychelles | Victoria | Africa |
| 48 | Croatia | Zagreb | Europe |
| 49 | Lithuania | Vilnius | Europe |
| 50 | Trinidad and Tobago | Port of Spain | North America |
| 51 | Qatar | Doha | Asia |
| 52 | Antigua | St. John's | North America |
| 53 | Latvia | Riga | Europe |
| 54 | Mexico | Mexico City | North America |
| 55 | Cuba | Havana | North America |
| 56 | Belarus | Minsk | Europe |
| 57 | Panama | Panama | North America |
| 58 | Belize | Belmopan | North America |
| 59 | Malaysia | Kuala Lumpur | Asia |
| 60 | Russian Federation | Moscow | Europe |
| 61 | Dominica | Roseau | North America |
| 62 | Bulgaria | Sofia | Europe |
| 63 | Romania | Bucharest | Europe |
| 64 | Libya | Tripoli | Africa |
| 65 | Macedonia | Skopje | Europe |
| 66 | Saint Lucia | Castries | North America |
| 67 | Mauritius | Port Louis | Africa |
| 68 | Colombia | Bogota | South America |
| 69 | Venezuela | Caracas | South America |
| 70 | Thailand | Bangkok | Asia |
| 71 | Saudi Arabia | Riyadh | Asia |
| 72 | Fiji | Suva | Australia and Oceania |
| 73 | Brazil | Brasilia | South America |
| 74 | Suriname | Paramaribo | South America |
| 75 | Lebanon | Beirut | Asia |
| 76 | Armenia | Yerevan | Asia |
| 77 | Philippines | Manila | Asia |
| 78 | Oman | Muscat | Asia |
| 79 | Kazakhstan | Astana | Asia |
| 80 | Ukraine | Kyiv | Europe |
| 81 | Georgia | Tbilisi | Asia |
| 82 | Peru | Lima | South America |
| 83 | Grenada | St. George's | North America |
| 84 | Maldives | Male | Asia |
| 85 | Türkiye | Ankara | Asia |
| 86 | Jamaica | Kingston | North America |
| 87 | Turkmenistan | Ashgabat | Asia |
| 88 | Azerbaijan | Baku | Asia |
| 89 | Sri Lanka | Colombo | Asia |
| 90 | Paraguay | Asuncion | South America |
| 91 | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Kingstown | North America |
| 92 | Albania | Tirana | Europe |
| 93 | Ecuador | Quito | South America |
| 94 | Dominican Republic | Santo Domingo | North America |
| 95 | Uzbekistan | Tashkent | Asia |
| 96 | China | Beijing | Asia |
| 97 | Tunisia | Tunisia | Africa |
| 98 | Iran | Tehran | Asia |
| 99 | Jordan | Amman | Asia |
| 100 | Cape Verde | Praia | Africa |
| 101 | Samoa | Apia | Australia and Oceania |
| 77 | Philippines | Manila | Asia |
| 78 | Oman | Muscat | Asia |
| 79 | Kazakhstan | Astana | Asia |
| 80 | Ukraine | Kyiv | Europe |
| 81 | Georgia | Tbilisi | Asia |
| 82 | Peru | Lima | South America |
| 83 | Grenada | St. George's | North America |
| 84 | Maldives | Male | Asia |
| 85 | Türkiye | Ankara | Asia |
| 86 | Jamaica | Kingston | North America |
| 87 | Turkmenistan | Ashgabat | Asia |
| 88 | Azerbaijan | Baku | Asia |
| 89 | Sri Lanka | Colombo | Asia |
| 90 | Paraguay | Asuncion | South America |
| 91 | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Kingstown | North America |
| 92 | Albania | Tirana | Europe |
| 93 | Ecuador | Quito | South America |
| 94 | Dominican Republic | Santo Domingo | North America |
| 95 | Uzbekistan | Tashkent | Asia |
| 96 | China | Beijing | Asia |
| 97 | Tunisia | Tunisia | Africa |
| 98 | Iran | Tehran | Asia |
| 99 | Jordan | Amman | Asia |
| 100 | Cape Verde | Praia | Africa |
| 101 | Samoa | Apia | Australia and Oceania |
| 102 | Kyrgyzstan | Bishkek | Asia |
| 103 | Guyana | Georgetown | South America |
| 104 | Salvador | San Salvador | North America |
| 105 | Moldova | Kishinev | Europe |
| 106 | Algeria | Algeria | Africa |
| 107 | South Africa | Pretoria | Africa |
| 108 | Syria | Damascus | Asia |
| 109 | Vietnam | Hanoi | Asia |
| 110 | Indonesia | Jakarta | Asia |
| 111 | Equatorial Guinea | Malabo | Africa |
| 112 | Tajikistan | Dushanbe | Asia |
| 113 | Mongolia | Ulaanbaatar | Asia |
| 114 | Bolivia | La Paz | South America |
| 115 | Egypt | Cairo | Africa |
| 116 | Honduras | Tegucigalpa | North America |
| 117 | Gabon | Libreville | Africa |
| 118 | Nicaragua | Managua | North America |
| 119 | Sao Tome and Principe | Sao Tome | Africa |
| 120 | Guatemala | Guatemala | North America |
| 121 | Solomon islands | Honiara | Australia and Oceania |
| 122 | Namibia | Windhoek | Africa |
| 123 | Morocco | Rabat | Africa |
| 124 | India | Delhi | Asia |
| 125 | Swaziland | Mbabane | Africa |
| 126 | Botswana | Gaborone | Africa |
| 127 | Myanmar | Naypyitaw | Asia |
| 128 | Zimbabwe | Harare | Africa |
| 129 | Ghana | Accra | Africa |
| 130 | Cambodia | Phnom Penh | Asia |
| 131 | Vanuatu | Vila | Australia and Oceania |
| 132 | Lesotho | Maseru | Africa |
| 133 | Papua New Guinea | Port Moresby | Australia and Oceania |
| 134 | Kenya | Nairobi | Africa |
| 135 | Cameroon | Yaounde | Africa |
| 136 | Congo | Brazzaville | Africa |
| 137 | Comoros | Moroni | Africa |
| 138 | Pakistan | Islamabad | Asia |
| 140 | Butane | Thimphu | Asia |
| 141 | Togo | Lome | Africa |
| 142 | Nepal | Kathmandu | Asia |
| 143 | Laos | Vientiane | Asia |
| 144 | Yemen | Sana | Asia |
| 145 | Bangladesh | Dhaka | Asia |
| 146 | Haiti | Port-au-Prince | North America |
| 147 | Madagascar | Antananarivo | Africa |
| 148 | Nigeria | Abuja | Africa |
| 149 | Djibouti | Djibouti | Africa |
| 150 | Uganda | Kampala | Africa |
| 151 | Tanzania | Dodoma | Africa |
| 152 | Mauritania | Nouakchott | Africa |
| 153 | Zambia | Lusaka | Africa |
| 154 | Senegal | Dakar | Africa |
| 155 | Congo (Democratic Republic) | Kinshasa | Africa |
| 156 | Ivory Coast | Yamoussoukro | Africa |
| 157 | Eritrea | Asmara | Africa |
| 158 | Benin | Porto-Novo | Africa |
| 159 | Guinea | Conakry | Africa |
| 160 | Gambia | Banjul | Africa |
| 161 | Angola | Luanda | Africa |
| 162 | Rwanda | Kigali | Africa |
| 163 | Malawi | Lilongwe | Africa |
| 164 | Mali | Bamako | Africa |
| 165 | Central African Republic | Bangui | Africa |
| 166 | Chad | N'Djamena | Africa |
| 167 | Guinea-Bissau | Bissau | Africa |
| 168 | Ethiopia | Addis Ababa | Africa |
| 169 | Burkina Faso | Ouagadougou | Africa |
| 170 | Mozambique | Maputo | Africa |
| 171 | Burundi | Bujumbura | Africa |
| 172 | Niger | Niamey | Africa |
| 173 | Sierra Leone | Freetown | Africa |
Canada

- Nominal GDP: $1.73 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $1.9 trillion
Canada displaced Russia from tenth place in the ranking in 2015 and still maintains its position. In 2021, nominal GDP reached $1.73 trillion, and by 2023 it is expected to grow to $2.12 trillion.
Despite the great importance of the service segment, 68% of exports are industrial products. Canada places a strong emphasis on industry as a key driver of future economic growth.
The kingdom recorded growth of 3% in 2021, 1.9% in 2021, and 1.5% in 2021. The forecast for 2021 is an increase of 1.8%.
Russia

- Nominal GDP: $1.64 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $4.35 trillion
Russia is also one of the strongest economies in the world. Our country is the largest state, but only the eleventh in terms of nominal GDP. When considering GDP on a PPP basis, it is sixth.
The 1990s became a difficult period for the country's economy, which inherited devastated industry and agriculture.
In the 2000s, an increase of 7% was recorded, but this was due to the commodity boom. Energy dependence had a bad impact on Russia during the crisis times of 2008-2009 and 2014.
2016 ended with economic growth of 0.2%. In 2021, the country achieved growth of 1.6%, in 2021 – by 2.3%, in 2021 – by 1.1%. The Navy assumes that in 2021 Russia's nominal GDP will grow by 1.9%.
Characteristics
General characteristics of emerging economies:
- Low or middle income level, which is determined by economic growth and improvement in technology. The reason for this is that a high share of benefits is concentrated in a small group of people, i.e. in these countries benefits are distributed unevenly. And the more uneven this distribution is, the lower the standard of living.
- Low labor productivity due to lack of motivation of workers, low development of technology and outdated equipment.
- Unemployment is high and underemployment is high. This is due to an insufficient number of jobs and a small number of vacancies.
- The population of some countries of this type is growing rapidly. Although the death rate is higher than in advanced economies, population growth is driven by high birth rates. The population is growing most rapidly in African countries.
- Economic dependence on primary products (eg clean oil and gas). European countries, the USA and other developed countries concentrate their economies on the processing of raw materials and the production of secondary products.

- The economy depends on developed countries. These countries often need the technology and capital of developed countries, and they, in turn, can dictate their terms.
- Benefits are distributed unevenly. The largest share of finance is concentrated in the hands of large companies and oligarchs.
- Many developing countries lack natural resources and fertile land.
- Inefficient use of capital, finance and equipment.
- Restriction of business activities by the state.
South Korea

- Nominal GDP: $1.63 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $2.32 trillion
South Korea is known for such conglomerates as Hyundai and Samsung, but it is not only through their efforts that the republic has penetrated into the strongest economies in the world and has moved closer to the TOP 10. Over the past decades, the country has made incredible progress, becoming one of the global leaders in the field of high technology.
In the 1960s, South Korea was one of the poorest countries in terms of GDP per capita, and now ranks 32nd in the world for this indicator ($44,740). Industrialization and international trade already in 2004 brought it into the “trillionaire club.” In 2019, the South Korean economy grew by 2%.
Now it is one of the world's leading exporters. The country has also created excellent conditions for investing from abroad and doing business.
Best countries by standard of living in 2021: TOP 10
According to the 2021 Quality of Life Index, the top ten included 7 European countries and 2 Pacific countries.
Unlike last year, the ranking of countries by standard of living is headed by the same countries, but with minor changes - Estonia left the top, and Norway entered instead. According to the global Numbeo database, the TOP countries for living in 2021 are as follows: 1st place - Switzerland (IQR - 190.82). Switzerland is considered one of the countries with the best level of medicine in the world. The average life expectancy of its citizens is 83 years. This is a state with a stable and prosperous economy, financial and banking system, high level of education and career prospects. But real estate and the cost of living here are among the most expensive in the world.
2nd place – Denmark (IQL – 190.01). Denmark has a transparent and stable political system, a progressive taxation system, and free and high-quality healthcare. According to a UN report published in the spring of 2021, it is also among the TOP 3 happiest countries in the world. Denmark is considered the safest place to live, occupies a leading position among European countries in the ranking of doing business, and there is almost no corruption here. But although the level of wages of the population is high, the cost of living itself is one of the most expensive in the world.
3rd place – the Netherlands (IQL – 183.31). The Netherlands is distinguished by its tolerance, democracy and stable economy. It is quite easy to run a profitable business here, there is no corruption and a transparent taxation system. The level of medicine in this country is higher than in France or Germany, and a higher education diploma is highly valued outside the state.
4th place – Finland (IQL – 182.79). Finland is the happiest country according to the UN report mentioned above. It is included in the TOP 10 richest countries in Europe, has a high level of social security, legal transparency, security and economic development. However, bureaucracy and corruption are present in Finland. It is also quite expensive to live in, but it is often chosen as a second home by people from the post-Soviet countries.
5th place – Austria (IQL – 182.37). Thanks to its diverse economy, Austria offers extensive employment and business opportunities. It is among the TOP 5 countries in terms of medicine and safety. It occupies a leading position in terms of the level of tourist flow: it has beautiful nature and many attractions. It is also important that in many political disputes at the global level, Austria adheres to neutrality.
Spain

- Nominal GDP: $1.4 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $1.94 trillion
The Spanish economy consistently ranks 5th in terms of volume in Europe and is returning faster than Italy to the pre-crisis level of 2008. In the industry structure, 2/3 is occupied by services, 12% by industry, 2.3% by agriculture. One of the driving forces of the economy is tourism. Attendance in Spain has increased every year from 2009 to 2021.
Active growth is hampered by weakness in the information technology, electronics, and utilities sectors.
In 2021, real GDP growth was 3%, in 2021 – 2.6%, in 2019 – 2.2%. The IMF forecast for 2021 is an increase of 1.8%.
Australia

- Nominal GDP: $1.38 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $1.36 trillion
Australia has the largest economy in the Pacific and the ninth largest securities exchange by market capitalization in the world. It has been steadily increasing GDP since 2009.
In 2013, the country was 12th in the world in terms of GDP, by 2021 it was overtaken by South Korea and Spain. But also in 2021, Australia was the country with the highest median wealth per adult.
In 2021, GDP growth was 2.4%, in 2021 – 2.7%, in 2021 – 1.7%. For 2021, the forecast is 2.3%.
At the beginning of 2021, catastrophic wildfires hit the country. It is still impossible to fully assess the damage, but this will definitely become one of the obstacles to GDP growth.
The richest countries by GDP based on PPP
However, considering a country rich just because it has a high GDP is not entirely correct. The fact is that different countries use different pricing policies, and the level of inflation can also significantly depreciate the value of funds. Therefore, the IMF believes that it is more correct to calculate GDP taking into account purchasing power parity. After all, what is important is not so much the level of income of the country, but also how much the citizens of the state can buy with this money.
Due to this adjustment, the list of the richest countries in the world is slightly different (the value of GDP based on PPP in trillions of US dollars is indicated in brackets):
- 1st place - China (21.27) . And this takes into account the fact that over the past 3 years, China’s GDP, taking into account PPP, has fallen from 23 trillion.
- 2nd place - USA (18.5) , which is not surprising. The United States has the most developed and diversified economy in the world.
- 3rd place - India (8.72) . The country is developing rapidly and may soon surpass both the United States and China in key economic indicators.
- 4th place - Japan (4.93) . The gap from the first three leaders is almost 2 times. Despite the external prosperity, the Japanese economy has serious problems, and the country has yet to overcome them.
- 5th place - Germany (3.97) . Significant pressure on the economy of the most developed country of the European Union is exerted by its social obligations.
- 6th place – Russia (3.75) . Interestingly, in terms of nominal GDP, our country is only in 12th place.
- 7th place - Brazil (3.13) . The development of the largest state in South America has slowed down, but is still confidently moving forward.
- 8th place - Indonesia (3.08) . One of the new economic leaders in Asia, Indonesia is moving towards modernizing production and introducing new technologies.
- 9th place - Great Britain (2.78) . Europe's oldest economy is not slowing down, and the standard of living in the country is one of the highest in the world.
- 10th place - France (2.73) . France is only slightly inferior to Britain in terms of GDP based on PPP.
Thus, Russia, judging by this rating, is a fairly rich country. However, the growing poverty of the population denies this fact.
Mexico

- Nominal GDP: $1.27 trillion
- GDP based on PPP: $2.63 trillion
In 2001, Mexico was the eighth country in the world by nominal GDP. By 2004, it fell out of the top ten, and by 2009, it settled in 15th place.
The oil industry plays an important role in the economy of this country. Therefore, in 2015-2016, under the influence of unfavorable dynamics of oil prices, Mexico's nominal GDP decreased by 18.8%. This was followed by growth, and the country almost “won back” the lost time.
According to the IMF, in 2017-2018 Mexico's GDP grew by 2-2.1%, in 2021 - by 0.4%. For 2021, the forecast is 1.3%.
Read: Top 20 countries that live richer than others











