Listen to the recording
On August 15 of this year, air traffic with Switzerland was resumed. This again fueled interest on the part of domestic tourists. We will describe in detail how to apply for a visa to Switzerland in 2020 below. After all, in connection with the coronavirus pandemic, a number of restrictions have appeared that Russians will have to face and, unfortunately, come to terms with.
The beauty of Switzerland. Image from freepik.com
Restrictions due to COVID-19
Despite the resumption of regular air flights from both Russian capitals, not everyone can still get to Switzerland. Currently, due to the pandemic, entry into the country for Russians is limited. Only citizens of Switzerland, EU countries, holders of a residence permit and those who have permission for long-term study, treatment or work in the country have the right to it.
Admiring the country from a bird's eye view is, for now, the maximum available to most Russian citizens. Image from freepik.com
Entry into the country and transit on tourist/transit visas is currently prohibited for Russians. In addition, all persons arriving in Switzerland from countries with a poor epidemiological situation must undergo a 10-day quarantine. And although quarantine for Russians was lifted in August, it has again become mandatory since October.
Due to the changing coronavirus situation, entry rules are also changing regularly. You will find the latest information in the corresponding section of the official website of the Swiss Government.
Why Switzerland is against joining the EU
Despite the close cooperation between the EU and Switzerland, disagreements on many issues have not subsided. The European Union is trying to impose as much as possible the standards that Switzerland must comply with. The Swiss feel great within the framework of their domestic politics and economy, the course of which no one wants to radically change.
Based on the fact that EU countries are Switzerland's largest trading partners (imports - 80%, exports - 60%), it is forced to some extent accept the rules and conditions imposed by the association. At the same time, the state tries to maintain its long-term neutrality and not allow third parties to control certain spheres of the country’s life.

There are actually many reasons, but among the more significant ones are the following:
- The economic crisis that occurred in 2008 cast serious doubt on the feasibility of Switzerland's accession to the European Union. The Swiss, being outside of this association, survived the crisis much better than all EU countries. Compared to the increasing stagnation of the Union economy, Switzerland has stable GDP growth and a very low unemployment rate. The state successfully exports its products to Asian markets, which allows them to remain in the favorable pre-crisis regime. The Swiss are considered one of the happiest people on the planet, which they themselves confirm. And many are sure that they are happy because they did not join the EU.
- Banking secrecy. One of the reasons for the economic and financial success of Switzerland is its properly structured banking legislation, which has been kept a state secret for many years. The European Union has repeatedly tried to find out the data, but Switzerland remains unshakable on this issue. And when signing an agreement with him, you will have to reveal, if not all, then the most key cards.
- Free movement of EU citizens. This provision is part of a bilateral agreement between the European Union and the acceding country. Thus, there is a high probability of a massive influx of immigrants into any of the participating countries wishing to work in it.
- Swiss neutrality in foreign policy. The Swiss have taken a neutral position for many years, which has become their international legal status. They are not part of any military alliance. This position of the state also contradicts EU provisions.
Types of visas to Switzerland
Switzerland is a member of the Schengen Agreement. There are several types of visas, which fall into two main categories:
- Short-stay or Schengen visa (type C). Issued for short visits for tourism purposes, for business trips or visiting friends and relatives. Accordingly, tourist, business and visitor visas are subtypes of Schengen. Visa C is issued for a maximum of 90 days within six months. If you plan to visit other Schengen countries with such a permit, then entry must first be made to Switzerland, and this is where you should spend most of the time of the trip.
- Long-term or national visa (type D). Such a permit must be issued for long-term study, employment and contract work, family reunification, and marriage. Obtaining a D visa opens the way for foreigners to subsequently obtain a residence permit and citizenship of the country.
There are also two types of transit visas - A and B. They will be required for layovers in Switzerland when flying to countries outside the Schengen area. The first one is issued for a transfer without delays, the second one allows you to stay in the transit zone of the airport for up to 5 days.
Due to the difficult epidemiological situation, from the spring of 2021, the issuance of visas of all categories to citizens of third countries, including Russians, is limited/suspended. But the Swiss Government assures that with the improvement of the situation regarding the spread of coronavirus, the current situation will be changed.
Validity periods and renewal rules
Depending on the purpose for which the visa is issued, consular officers will determine its typology. To acquire a multiple-entry visa, you must prove the need for frequent stay in the country.

The validity of a transit visa does not exceed five days. A standard Schengen visa will allow you to stay in Europe for 90 days in one half-year. A national or work visa allows you to stay in the country for the entire duration of its validity.
It is possible to extend the period of validity of a visa under force majeure circumstances. To do this, you should contact your local migration office a few days before your expiring visa expires. Then go home and re-issue the document. Regardless of whether Switzerland is part of the European Union, it is possible to obtain a Schengen visa to any state in the visa-free zone and return to the Confederation.
Documents for visa C
Documents can be submitted through the Swiss Embassy in Moscow, visa centers or sent by mail through specialized DHL offices. Reception takes place by prior appointment. If we are talking about Schengen, then instead of the applicant, the package of papers can be handed over by his relative, representative or accredited travel agency. The applicant submits documents for a D visa in person to the Embassy - without any exceptions.
Residents of Kaliningrad and the region can apply for a visa to the Swiss Embassy in Latvia (Riga).
Document package for visa C to Switzerland:
- Application form filled out in Russian, German, English or French and signed by the applicant.
- A passport valid for at least 90 days after returning from a trip to Switzerland with at least two blank pages.
- Two photographs 35x45 mm with standard Schengen requirements. One photo must be pasted on the application form, the second must be submitted separately.
- A copy of all completed pages of the internal passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation.
- Medical insurance with coverage starting from 30,000 euros, valid for the entire period of stay in the country, as well as in other Schengen countries.
- Tickets or confirmation of their reservation, as well as a travel voucher for the duration of your stay in the country.
- Documents confirming financial solvency - from 100 Swiss francs (about 8,660 rubles) on the day of the visit.
The latter may be an official certificate from work about earnings covering travel expenses or a bank account statement. Confirmation from the sponsor will also come in handy if, for example, you are flying to visit.

Zurich Airport. In addition, you can now fly from Moscow to Geneva. Image from freepik.com
In case of a guest visit, you must additionally attach an invitation from the Swiss side with a copy of the inviting person’s passport. For training - a certificate of enrollment in courses, for participation in cultural and sports events - confirmation of participation from the organizer, and in the case of a business trip - a request from an organization in Switzerland. If you plan to find employment and work in the country, then in addition to contract documents you will also need permission from the local cantonal authorities.
Be sure to take the entire package of documents with you on your trip, since the likelihood of them being checked upon arrival in the country is very high.
Types of Swiss visas
Different types of documents will be required for different purposes of visiting the Swiss Confederation. Depending on what kind of visa the applicant will need to apply for, a list of required documents is compiled.
Airport transit visa to Switzerland
Citizens transiting Switzerland must obtain a special transit visa. If your final destination country is part of the Schengen area, you will not need to obtain a separate entry document. In this case, you are allowed to be in the air hub area without special documents.
Regular entry visa to Switzerland
This Schengen visa is issued by Switzerland to citizens for a wide range of purposes, such as meeting relatives or friends, tourism, participating in cultural and sporting events, studying on short courses or attending conferences. Depending on the task, Schengen visas are divided into several types:
- visit visa to Switzerland;
- tourist visa to Switzerland;
- business visa to Switzerland;
- medical visa to Switzerland;
- study visa to Switzerland for short-term courses;
- visa for participants in sporting events;
- visa for participants in cultural events;
- visa for formal official visits;
- transit visa category “C”.
Russians who have diplomatic passports and plan to visit the country on an official visit do not need to apply for this type of Swiss visa. A permit will not be required for holders of a valid residence permit issued by a Schengen member country.

National visa
This type of visa should be issued for long-term stay in the state. It is suitable for marriage with citizens of the state for the purpose of further residence, long-term study at universities, family reunion or long visits based on an invitation letter. A national visa to Switzerland is issued solely on the basis of permission from the country’s migration service.
Work permit
This type of visa allows its holder to carry out legal work activities in Switzerland under an employment contract. You will be able to receive it only after a positive decision is made from the Cantonal Migration Service.
Processing times and cost of a visa to Switzerland
The Embassy usually takes 3 days , after which a decision is made. When submitting papers through a visa center or post offices, you must also take into account the delivery time. Then the processing time may take up to 7 days. In exceptional cases, if the package is suspicious and the verification requires the involvement of Swiss law enforcement officers, the review can last up to 90 days.
The cost of a visa is fixed and amounts to 35 euros for citizens of Russia, Ukraine, Georgia and Moldova. Children under 6 years of age and citizens of Ukraine under 18 years of age can receive it for free.
Officially, the Swiss Embassy does not provide an urgent visa service. But in emergency cases (threat to life and health), you need to fill out a special form and submit a request for an expedited review procedure to the email address .
You can track the readiness of your visa in your personal account on the official website of the Embassy. Also, information about the final decision is sent by e-mail and in the form of a text message to the phone.
Applying for a national visa D
The basis of the package of documents for a national visa is the same as for applying for a Schengen visa. But additional paperwork will also be required. Their composition depends on the purpose of the visit (training, employment, family reunification, etc.). A complete list of documents is presented in the corresponding section of the official website of the Swiss Government. But be prepared for the fact that you will be asked to provide some of the documents that are not on the list - the review process in the case of a D visa is purely individual.

The National D visa is the first step to obtaining a national passport. Image from freepik.com
Applying for a visa for a child
Children can cross the borders of other countries if they have permission to enter. To obtain a visa you will need the following package of documents:
- Birth certificate. For children over the age of 14, a personal passport is required. The certificate is accompanied by a copy of it, certified by a notary and translated into any of the official languages of Switzerland;
- Two copies of the questionnaire;
- Medical policy;
- Two photographs (the requirements for the photo are the same as for images of adults).
Previously, there was a practice of including children under six years of age on the pages of their parents’ foreign passports. Modern rules for entry into Switzerland require that the child have a personal document.

Swiss chocolate is a symbol of the Alpine Republic, along with Swiss cheese and Swiss watches. Chocolate appeared in Switzerland at the end of the 17th century as a bitters medicine, using the medicinal properties of cocoa. Later, the Swiss came up with the idea of making the medicine sweet. This medicine was used to treat anemia, anemia, and loss of strength. Switzerland is one of the first countries to show interest in the product. In the chocolate museum you can learn not only the history of the origin of the confectionery product, but also directly observe the process of its production.
If children cross the border with only one parent, the other must give permission to leave.
If the parents are not married, you must take with you a certificate confirming this fact.
If the child does not have a second parent, this will need to be documented at the border. A death certificate, a certification that the person is listed as missing, or a certificate from the registry office are suitable for this.
A D visa requires travel permission from each parent.

Local ski resorts are a global example of an integrated approach to organizing recreation, which takes into account the needs of people of different physical shape and age. In the case when a minor crosses the border with an accompanying person, the latter must have a power of attorney with him. You will also need photocopies of the passports of the child’s parents, their permission to travel, and confirmation of their financial capabilities. If the trip is paid for by an outsider, you must present a letter from the sponsor.
All certificates or permissions from parents must be translated into English, French, Italian or German and have a notary stamp.
Switzerland visa refusal
The Alpine Confederation strictly approaches compliance with migration legislation. Therefore, refusal, ban or cancellation is common. Common reasons for refusal:
- Lack of necessary documents.
- Errors in filling out the form.
- Providing false information.
- Failure to meet financial independence requirements.
- Lack of confirmation or discrepancy with the purpose of the visit specified in the application form.
- Violations of visa laws that the applicant already has.
- Problems with the law in Russia, Switzerland or Europe.
The last two points may even become a reason for a ban on visiting the Schengen zone (the so-called “visa quarantine”) or cancellation of a previously issued visa permit. The most terrible stamp on documents - “C-4” - means a lifelong ban on visiting the Schengen countries.
An interesting video about how to get Schengen during quarantine.
Subscribe to Migrantu Mir: Yandex News.
Difference between the European Union, Eurozone and Schengen Area
These three associations have far from the same goals and objectives. Countries that are in the EU may not be members of the Eurozone or the Schengen area and vice versa. To understand the differences between them, you need to understand the purpose of each individual formation.
Eurozone
The Eurozone is a monetary union operating within the EU. It unites 19 countries of the European Union, Monaco, Vatican City, San Marino and Andorra, which are not members of the European Union. There is a single currency throughout the territory - the euro.
Countries that previously depended on European currencies - the German mark, the French franc and the Spanish peseta - switched to payments in euros.
Iraq, Cuba, North Korea and Syria have chosen the euro for non-cash payments.
The European Central Bank is responsible for all aspects of monetary policy in the European Union and the eurozone. Budget audits are carried out by the European Court of Auditors.
European Union
The EU is an economic and political union of 28 European states. The purpose of this union is the integration of European states into a single economic market, as well as the absence of passport and visa control and the use of a common currency, the Euro.
Since July 1, 2013, the union includes 28 states: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Great Britain, Hungary, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Spain, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania , Slovakia, Slovenia, Finland, France, Croatia, Czech Republic, Sweden and Estonia.
There are currently three agreements that provide varying degrees of integration within the European Union:
- EU membership;
- membership in the Euro Area;
- participation in the Schengen agreement.
It is important to clarify that:
- EU membership does not necessarily entail participation in the Schengen Agreement;
- Not all EU member states are part of the Euro Area.
Let us give an example of varying degrees of integration: for example, Great Britain, Denmark and Sweden did not consider it necessary to join the euro zone and retained the circulation of their national currency. And Norway, Iceland, Switzerland and Liechtenstein are not members of the European Union, but are included in the Schengen area.
The main distinguishing principle of the EU from other international organizations is the existence of its own law.
It directly regulates relations not only between EU member states, but also their citizens and legal entities. The basic achievements of EU law can be considered the institution of four freedoms: freedom of movement of persons, freedom of movement of capital, freedom of movement of goods and freedom of provision of services in these countries.
Current list of countries
Currently the EU includes (the year of accession is indicated in brackets):
- Austria (1995)
- Belgium (1957)
- Bulgaria (2007)
- UK (1973)
- Hungary (2004)
- Germany (1957)
- Greece (1981)
- Denmark (1973)
- Ireland (1973)
- Spain (1986)
- Italy (1957)
- Cyprus (2004)
- Latvia (2004)
- Lithuania (2004)
- Luxembourg (1957)
- Malta (2004)
- Netherlands (1957)
- Poland (2004)
- Slovakia (2004)
- Slovenia (2004)
- Portugal (1986)
- Romania (2007)
- Finland (1995)
- France (1957)
- Croatia (2013)
- Czech Republic (2004)
- Sweden (1995)
- Estonia (2004)
Schengen Area
Back in 1985, many countries around the world signed an agreement regulating visa-free travel between these states.
The agreement was signed in a small village called Schengen, which is why the agreement has such a name.
The signing of the agreement took place on the territory of Luxembourg.
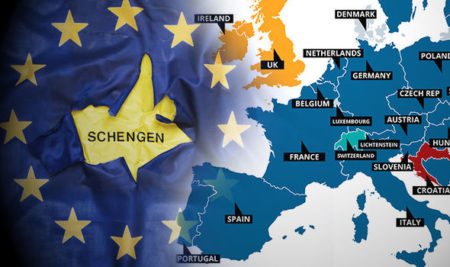
Despite the fact that the document was signed in 1985, the Schengen rules began to apply only in 1995 . The Swiss Confederation signed the treaty in 1996.










